Question 1
1. Which statement describes dense irregular connective tissue?
Choices:
- Its fibres are arranged into an interwoven meshwork sheet that has tensile strength in all directions.
- It forms tendons and ligaments.
- It lacks a blood supply, and therefore gets oxygen and nutrients by diffusion from surrounding tissues.
- It is more ground substance than fibres, by volume.
Answers:
- Its fibres are arranged into an interwoven meshwork sheet that has tensile strength in all directions.
Comments:
- Correct
- That’s right! Dense irregular connective tissue is dominated by collagen type I fibres arranged in a meshwork sheet. Because fibres run in all directions, tensile strength is imparted in all directions as well.
- Continue
Question 2
2. From the options listed below, choose the factors that can contribute to edema.
Choices:
- Increased vascular permeability
- Congestion of lymph nodes
- Obstruction of lymph flow
- Liver disease or damage
- Decreased venous pressure
- Elevated plasma protein levels
Answers:
- Increased vascular permeability
- Congestion of lymph nodes
- Obstruction of lymph flow
- Liver disease or damage
Comments:
- Correct
- That’s right! Edema is caused by increased production of tissue fluid or decreased clearance of tissue fluid.
- Continue
Question 3
3. What is the function of fibroblasts?
Choices:
- Store lipids
- Release mediators of inflammation
- Differentiate into antigen presenting cells following antigen exposure
- Produce fibres & organic components of GS
- They are multipotent stem cells
Answers:
- Produce fibres & organic components of GS
Comments:
- Correct
- That’s right! Fibroblasts produce the organic molecules of ground substances and fibres (collagen, elastin).
- Continue
Question 4
4. What is the function of B-lymphocytes?
Choices:
- Store lipids
- Release mediators of inflammation
- Differentiate into antibody-producing plasma cells following antigen exposure
- Produce fibres & organic components of GS
- They are multipotent stem cells
Answers:
- Differentiate into antibody-producing plasma cells following antigen exposure
Comments:
- Correct
- That’s right! B lymphocytes differentiate into antibody-producing plasma cells upon antigen exposure.
- Continue
Question 5
5. What is the function of macrophages?
Choices:
- Phagocytic and antigen presenting cells that are derived from blood monocytes
- Release mediators of inflammation
- Differentiate into antibody-producing plasma cells following antigen exposure
- Produce fibres & organic components of GS
- They are multipotent stem cells
Answers:
- Phagocytic and antigen presenting cells that are derived from blood monocytes
Comments:
- Correct
- That’s right! Macrophages are derived from blood monocytes. They are phagocytic and present antigens to lymphocytes.
- Continue
Question 6
6. What is the function of adipocytes?
Choices:
- Phagocytic and antigen presenting cells that are derived from blood monocytes
- Release mediators of inflammation
- Differentiate into antibody producing plasma cells following antigen exposure
- Produce fibres & organic components of GS
- They store lipids
Answers:
- They store lipids
Comments:
- Correct
- That’s right! Adipocyte stores triglycerides in a single, large lipid droplets within the cell.
- Continue
Question 7
7. What is the function of mast cells?
Choices:
- Phagocytic and antigen presenting cells that are derived from blood monocytes
- Release mediators of inflammation
- Differentiate into antibody producing plasma cells following antigen exposure
- Produce fibres & organic components of GS
- They store lipids
Answers:
- Release mediators of inflammation
Comments:
- Correct
- That’s right! Sensitized mast cells release mediators of inflammation (histamine, chemotactic factors) upon encountering antigen.
- Continue
Question 8
8. What is the function of mesenchymal cells?
Choices:
- Phagocytic and antigen presenting cells that are derived from blood monocytes
- They are multipotential stem cells
- Differentiate into antibody producing plasma cells following antigen exposure
- Produce fibres & organic components of GS
- They store lipids
Answers:
- They are multipotential stem cells
Comments:
- Correct
- That’s right! Mesenchymal cells are multipotential stem cells that can differentiate into different cell types (fibroblasts, osteoblasts, adipocytes etc.).
- Continue
Question 9
9. Which statement describes microphages?
Choices:
- Phagocytic and antigen presenting cells that are derived from blood monocytes
- They are multipotential stem cells
- Differentiate into antibody producing plasma cells following antigen exposure
- They respond to chemotactic signals to migrate from the blood into CT spaces
- They store lipids
Answers:
- They respond to chemotactic signals to migrate from the blood into CT spaces
Comments:
- Correct
- That’s right! Microphages such as neutrophils and eosinophils circulate in blood. They response to chemotactic signals to migrate into CT space, where tissue damage/ inflammation has occurred.
- Continue
Question 10
10. The matrix of ordinary connective tissue is highly hydrated, due to the hydrophilic nature of its ___________.
Choices:
- Adhesive glycoproteins
- Elastic fibres
- Fibrocytes
- Proteoglycans
- Collagen fibres
- Integrins
Answers:
- Proteoglycans
Comments:
- Correct
- That’s right! Proteoglycans are negatively charged and highly hydrophilic molecules. GS gel-like consistency is caused by the tight binding of water to proteoglycan.
- Continue
Question 11
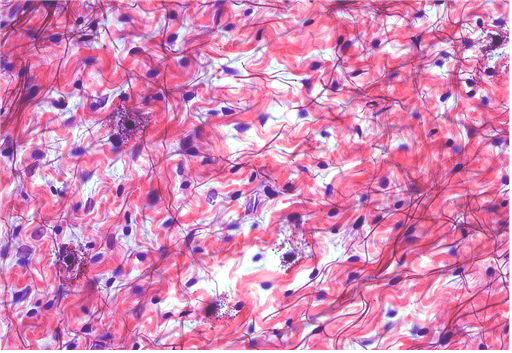
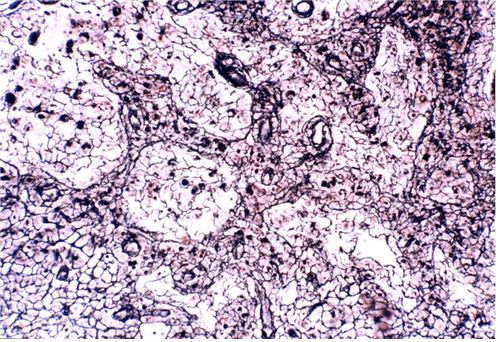
11. Identify the class of tissue. Be specific.
Choices:
- Dense Regular CT
- Dense Irregular CT
- Elastic CT
- Reticular CT
- Areolar CT
Answers:
- Areolar CT
Comments:
- Correct
- That’s right! Areolar CT can be identified by the variety of cell and fibre types. In addition, GS occupies a large volume of the tissue, as represented by the white space.
- Continue
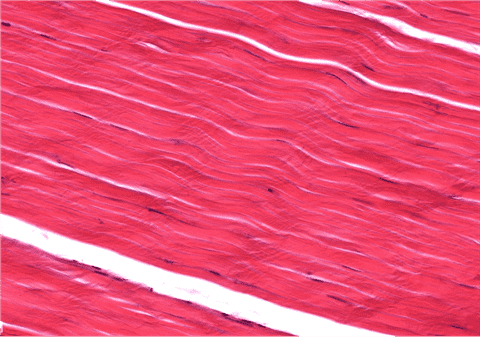
Question 12
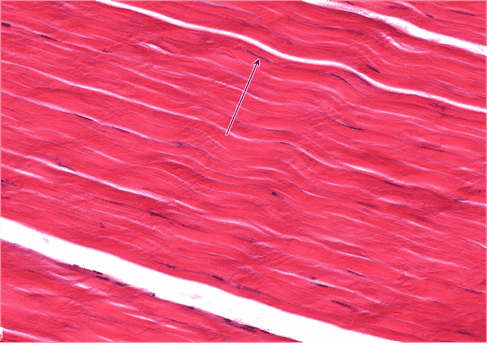
12. Identify the class of tissue. Be specific.
Choices:
- Dense Regular CT
- Dense Irregular CT
- Elastic CT
- Reticular CT
- Areolar CT
Answers:
- Dense Regular CT
Comments:
- Correct
- That’s right! Dense Regular CT largely consists of collagen type I fibres arranged in parallel arrays. Fibrocytes can be identified by the flattened and elongated nuclei.
- Continue
Question 13
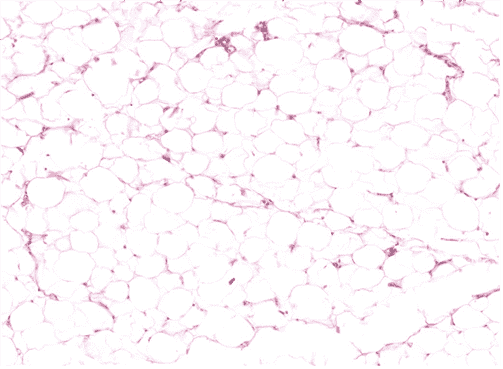
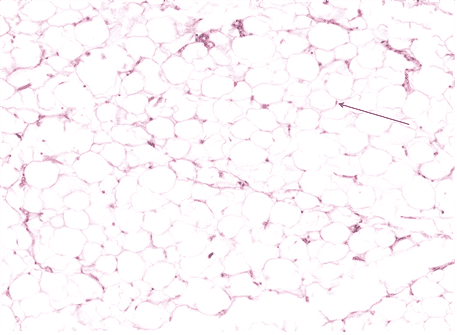
13. Identify the class of tissue. Be specific.
Choices:
- Dense Regular CT
- Adipose CT
- Elastic CT
- Reticular CT
- Areolar CT
Answers:
- Adipose CT
Comments:
- Correct
- That’s right! Adipose CT can be identified by the signet ring-like appearance, where the nucleus is pushed to the side and intracellular space is empty due to lipid extraction during tissue processing.
- Continue
Question 14
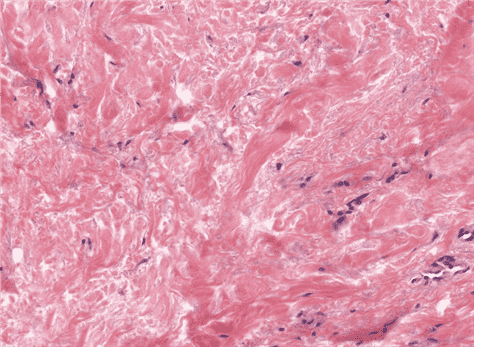
14. Identify the class of tissue. Be specific.
Choices:
- Dense Regular CT
- Elastic CT
- Reticular CT
- Dense Irregular CT
- Areolar CT
Answers:
- Dense Irregular CT
Comments:
- Correct
- That’s right! The coarse bundles of collagen type I fibres running in and out of plane is characteristic of dense irregular CT.
- Continue
Question 15
15. Identify the class of tissue. Be specific.
Choices:
- Dense Regular CT
- Dense Irregular CT
- Loose CT
- Reticular CT
- Elastic CT
Answers:
- Reticular CT
Comments:
- Correct
- That’s right! Reticular fibres dominate in reticular CT, where it forms a stroma which supports the tissue parenchyma.
- Continue
Question 16
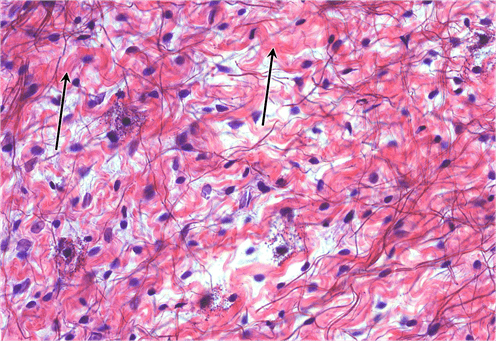
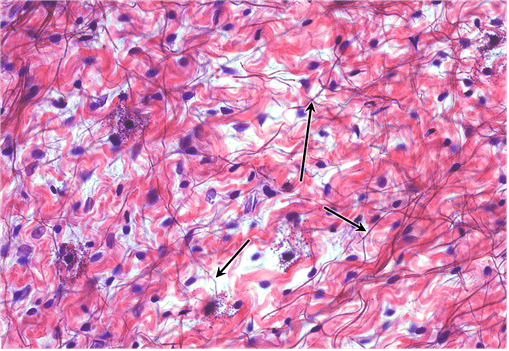
16. Identify the fibre type at the tips of the arrows. Be specific.
Choices:
- collagen type I
- collagen type I fibres
- type I collagen
- type I collagen fibres
Answers:
- collagen type I
- collagen type I fibres
- type I collagen
- type I collagen fibres
Comments:
- Correct
- That’s right! Collagen type I forms wavy fibres that disperse abundantly in loose areolar CT.
- Continue
Question 17
17. Identify the darker structure at the tip of the arrow.
Choices:
- Lymphocyte
- Macrophage
- Mesenchymal cell nucleus
- Nucleus of Adipocyte
Answers:
- Nucleus of Adipocyte
Comments:
- Correct
- That’s right! Adipocytes appears like a ring with their darker stained nuclei pushed to the side.
- Continue
Question 18
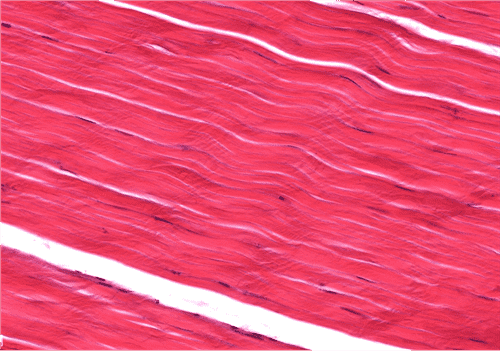
18. Identify the cell type indicated by the arrow.
Choices:
- fibrocyte
- fibrocytes
- fibroblasts
- fibroblast
Answers:
- fibrocyte
- fibrocytes
- fibroblasts
- fibroblast
Comments:
- Correct
- That’s right! Dense regular CT consists of collagen type I fibres arrange in parallel arrays. Fibrocytes are usually squeezed between the fibres therefore only their elongated nuclei can be seen.
- Continue
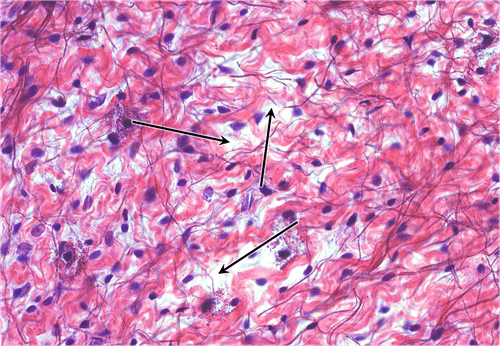
Question 19
19. Identify the fibre type at the tips of the arrows. Be specific.
Choices:
- elastic
- elastic fibre
- elastic fibres
Answers:
- elastic
- elastic fibre
- elastic fibres
Comments:
- Correct
- That’s right! Elastic fibres appear as the fine, straight and dark-stained fibres scattered in loose areolar CT.
- Continue
Question 20
20. What fibre type dominates in this tissue? Be specific.
Choices:
- collagen type I
- collagen type I fibres
- type I collagen
- type I collagen fibres
Answers:
- collagen type I
- collagen type I fibres
- type I collagen
- type I collagen fibres
Comments:
- Correct
- That’s right! Dense regular CT is dominated by collagen type I fibres.
- Continue
Question 21
21. In life, what fills the empty spaces indicated by the arrows?
Choices:
- ground substance
Answers:
- ground substance
Comments:
- Correct
- That’s right! Ground substance fills the empty spaces in the loose areolar CT.
- Continue
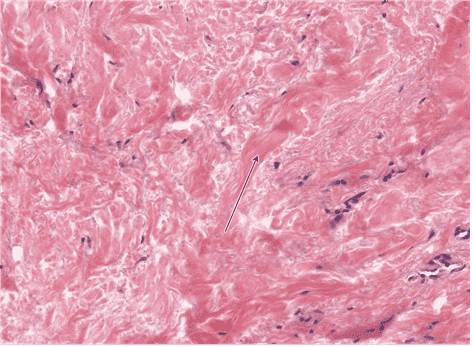
Question 22
22. Identify the fibre type at the tip of the arrow. Be specific.
Choices:
- collagen type I
- type I collagen
Answers:
- collagen type I
- type I collagen
Comments:
- Correct
- That’s right! Dense irregular CT is largely made of collagen type I fibres that run in and out of plane of section.
- Continue
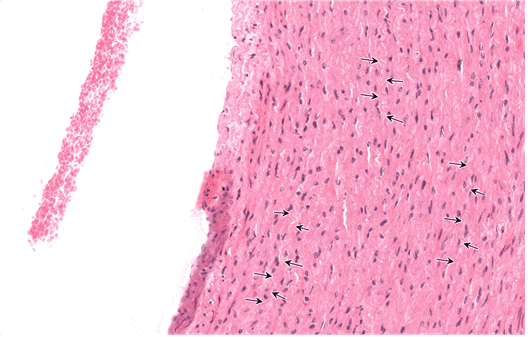
Question 23
23. Identify the fibre type at the tip of the arrows. Be specific.
Choices:
- elastic fibres
- elastic fibre
Answers:
- elastic fibres
- elastic fibre
Comments:
- Correct
- That's right! Elastic fibres can be found in elastic CT. In the absence of fibrillin (i.e in elastic artery), elastic fibres form fenestrated sheets, which resemble lasagne noodles in the image.
- Continue