Question 1
1. From the options listed below, choose the CORRECT statement(s) regarding cartilage.
Choices:
- Cartilages withstand compressive force because of the highly hydrated nature of its matrix.
- Unlike most connective tissues, cartilages contain more cells than matrix.
- Cartilage plays a role in intramembraneous ossification.
- Cartilages produce ATP largely by aerobic means.
- Cartilage is avascular but innervated.
Answers:
- Cartilages withstand compressive force because of the highly hydrated nature of its matrix.
Comments:
- Correct
- That’s right! GAGs within the cartilages tightly bind water and therefore permit cartilages to withstand compressive forces.
- Continue
Question 2
2. From the options listed below, choose the CORRECT statement(s) regarding bone tissue.
Choices:
- Osteocytes are derived from osteoblasts.
- Osteocytes may be present on the surface of bone matrix.
- Bone tissue is avascular and therefore dependent on diffusion of metabolites from surrounding tissues for its needs.
- The collagen fibre content of its matrix imparts it with compressional strength.
- It can withstand a certain amount of bending, owing to the inorganic salts in its matrix.
- In compact bone, matrix is organized in lamellae, whereas in spongy bone it is not.
Answers:
- Osteocytes are derived from osteoblasts.
Comments:
- Correct
- That’s right! Osteocytes are fully differentiated bone cells derived from osteoblasts.
- Continue
Question 3
3. From the options listed below, choose the component(s) of an osteon.
Choices:
- Canaliculi
- Osteocytes
- Concentric lamellae
- Central canal
- Osteoclasts
- Osteoblasts
- Perforating canal
- Circumferential lamellae
- Interstitial lamellae
Answers:
- Canaliculi
- Osteocytes
- Concentric lamellae
- Central canal
Comments:
- Correct
- That’s right! An osteon consists of a central canal surrounded by multiple layers of concentric lamellae. Ostocytes are located between adjacent lamellae, and extend their cell processes through the bone matrix in canaliculi.
- Continue
Question 4
4. The dominant cell type in the fibrous layer of the periosteum is the _____________.
Choices:
- Osteoprogenitor cells
- Osteoblasts
- Osteoclasts
- Bone-lining cells
- Fibrocytes
Answers:
- Fibrocytes
Comments:
- Correct
- That’s right! Fibrocytes are the dominant cell type in the fibrous layer of periosteum. They produce collagen type I, forming the dense irregular CT layer that is periosteum.
- Continue
Question 5
5. What substance in the ECM of cartilage binds aggrecan monomers?
Choices:
- Type II collagen fibrils
- Chondrocytes
- Hyaluronic Acid
- Bone-lining cells
- Fibrocytes
Answers:
- Hyaluronic Acid
Comments:
- Correct
- That’s right! Aggrecan monomers link to hyaluronic acid, forming massive proteoglycan aggregates.
- Continue
Question 6
6. Identify the class of tissue. Be specific.
Choices:
- Articular cartilage
- Fibrocartilage
- Elastic cartilage
- Bone
Answers:
- Articular cartilage
Comments:
- Correct
- That’s right! Articular cartilage is hyaline cartilage that lacks a perichondrium.
- Continue
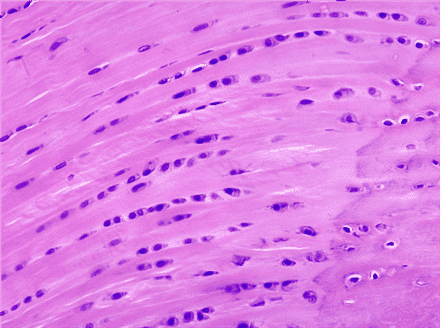
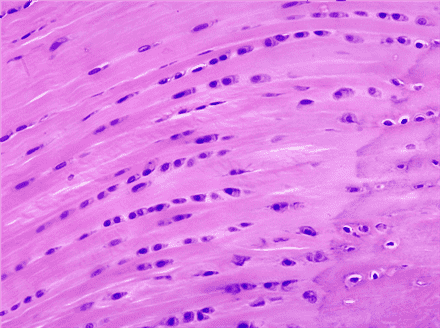
Question 7
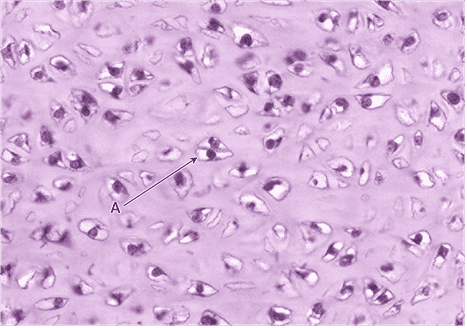
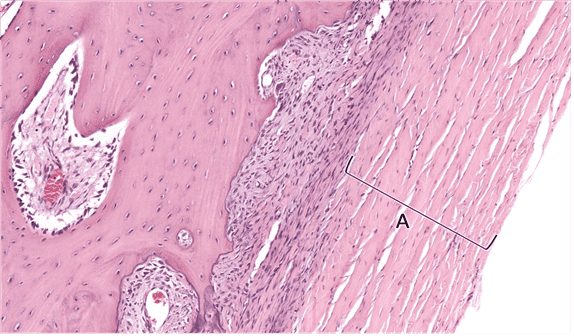
7. Name the dominant cell type in this tissue as indicated by A.
Choices:
- chondrocyte
- chondrocytes
Answers:
- chondrocyte
- chondrocytes
Comments:
- Correct
- That’s right! Chondrocytes are found in cartilage.
- Continue
Question 8
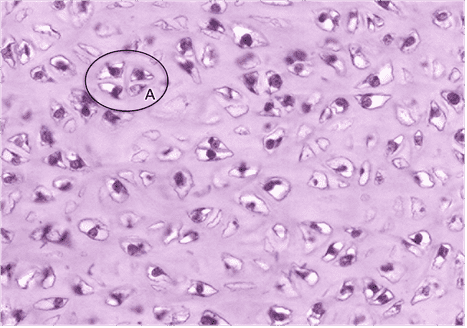
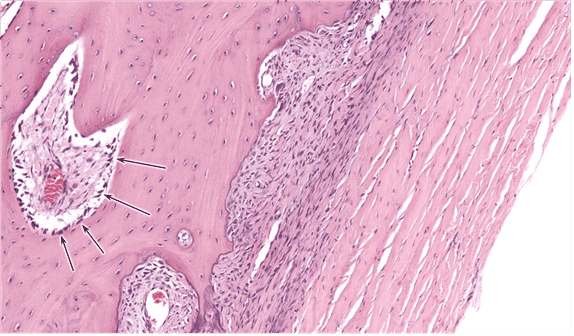
8. What is encircled in black? Be specific.
Choices:
- isogenous group
- isogenous
Answers:
- isogenous group
- isogenous
Comments:
- Correct
- That’s right! Mature chondrocytes can form isogenous groups.
- Continue
Question 9
9. What is the dominant fibre type in tissue A?
Choices:
- type II collagen
- collagen type II
- collagen II
- collagen type II fibrils
- collagen type II fibres
- collagen II fibrils
- collagen II fibres
- type II collagen fibrils
- type II collagen fibres
Answers:
- type II collagen
- collagen type II
- collagen II
- collagen type II fibrils
- collagen type II fibres
- collagen II fibrils
- collagen II fibres
- type II collagen fibrils
- type II collagen fibres
Comments:
- Correct
- That’s right! Collagen type II is specific to cartilage and is highly packed in the ECM of hyaline cartilage.
- Continue
Question 10
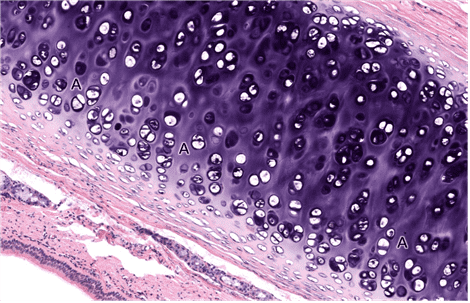
10. Identify the class of tissue. Be specific.
Choices:
- fibrocartilage
- fibrocartilage
Answers:
- fibrocartilage
- fibrocartilage
Comments:
- Correct
- That’s right! Fibrocartilage can be identified by the rows of rounded chondrocytes arranged between bundles of collagen fibres.
- Continue
Question 11
11. What is the dominant fibre type present in this tissue?
Choices:
- type I collagen
- collagen type I fibres
- collagen type I
- type I collagen fibres
Answers:
- type I collagen
- collagen type I fibres
- collagen type I
- type I collagen fibres
Comments:
- Correct
- That’s right! Collagen type I fibres dominate in fibrocartilage and impart tensile strength.
- Continue
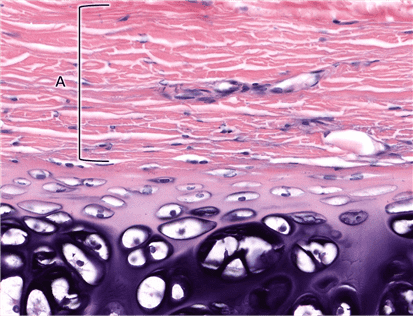
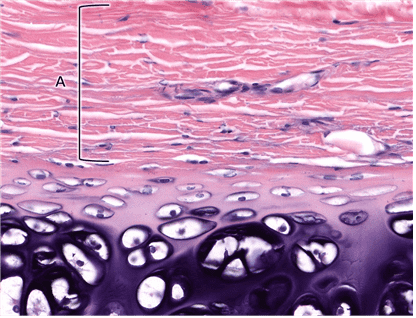
Question 12
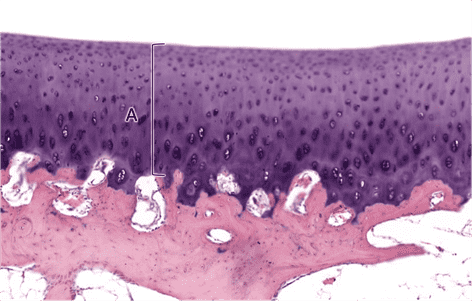
12. Identify layer A. Be specific.
Choices:
- Outer Fibrous Layer of Perichondrium
- Fibrous Perichondrium
- Outer Fibrous Layer
- Fibrous Layer of Perichondrium
- perichondrium, fibrous layer
- perichondrium, outer fibrous layer
Answers:
- Outer Fibrous Layer of Perichondrium
- Fibrous Perichondrium
- Outer Fibrous Layer
- Fibrous Layer of Perichondrium
- perichondrium, fibrous layer
- perichondrium, outer fibrous layer
Comments:
- Correct
- That’s right! The outer fibrous layer of perichondrium is made up of dense irregular connective tissue. This layer provides attachment of cartilage to adjacent tissue.
- Continue
Question 13
13. What is the main cell type in layer A?
Choices:
- Fibroblasts
- Fibroblast
- fibrocyte
- fibrocytes
Answers:
- Fibroblasts
- Fibroblast
- fibrocyte
- fibrocytes
Comments:
- Correct
- That’s right! Fibroblasts in the fibrous layer of perichondrium produce collagen fibres.
- Continue
Question 14
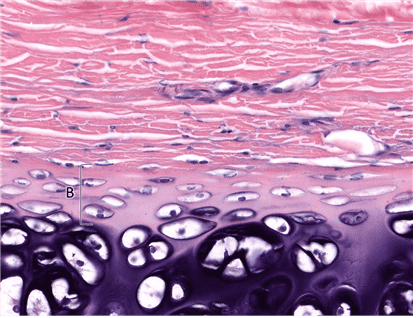
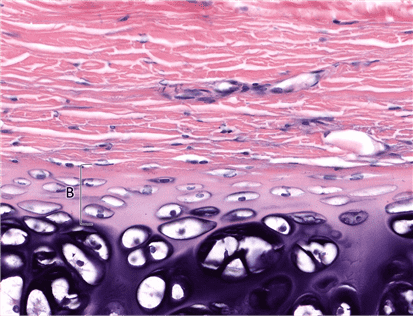
14. Identify layer B. Be specific.
Choices:
- Cellular Layer of Perichondrium
- Inner Cellular Layer of Perichondrium
- Cellular Perichondrium
- Inner Cellular Layer
Answers:
- Cellular Layer of Perichondrium
- Inner Cellular Layer of Perichondrium
- Cellular Perichondrium
- Inner Cellular Layer
Comments:
- Correct
- That’s right! The inner cellular layer of perichondrium contains chondroblasts, which contribute to appositional growth of cartilage.
- Continue
Question 15
15. What is the main cell type in layer B?
Choices:
- Chondroblast
- Chondroblasts
Answers:
- Chondroblast
- Chondroblasts
Comments:
- Correct
- That’s right! Chondroblasts are the main cell type in the inner cellular layer of perichondrium. They produce new matrix during appositional growth of cartilages.
- Continue
Question 16
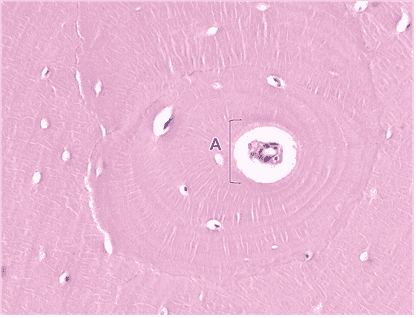
16. What is the specific name of space A?
Choices:
- Central canal
- Haversian Canal
Answers:
- Central canal
- Haversian Canal
Comments:
- Correct
- That’s right! The central (Haversian) canal is located at the center of an osteon. It contains BVs and Ns .
- Continue
Question 17
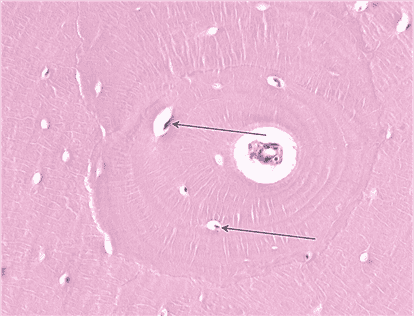
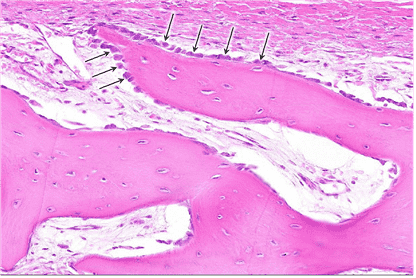
17. Identify the structures indicated by the arrows.
Choices:
- Canaliculi
Answers:
- Canaliculi
Comments:
- Correct
- That’s right! A dense network of canaliculi ramifies throughout bone matrix to facilitate molecular exchange. Cell processes of osteocytes are located within the canaliculi.
- Continue
Question 18
18. Identify the cell type indicated by the arrows.
Choices:
- Osteocytes
- Osteocyte
Answers:
- Osteocytes
- Osteocyte
Comments:
- Correct
- That’s right! Osteocytes are located between adjacent lamellae and extend their processes into the canaliculi.
- Continue
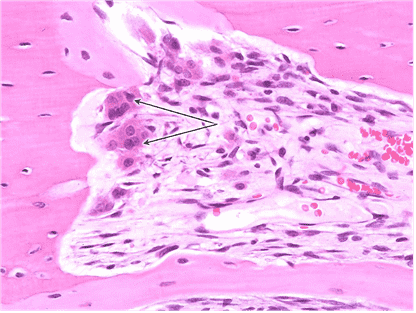
Question 19
19. Identify the cells indicated by the arrows.
Choices:
- Osteoblasts
Answers:
- Osteoblasts
Comments:
- Correct
- That’s right! Osteoblasts are cuboid to columnar cells located on the surface of existing bone matrix.
- Continue
Question 20
20. What is the name of the spaces that contains these cells?
Choices:
- Lacuna
- Lacunae
Answers:
- Lacuna
- Lacunae
Comments:
- Correct
- That’s right! Lacunae are the spaces within the bone matrix occupied by osteocytes. In a lacuna, a fine layer of unmineralized matrix surrounds the osteocyte.
- Continue
Question 21
21. Identify the cell type indicated by the arrows.
Choices:
- Osteoclast
- Osteoclasts
Answers:
- Osteoclast
- Osteoclasts
Comments:
- Correct
- That’s right! Osteoclasts are multinucleated cells found in resorption lacunae on the surface of existing bone matrix. This cell type aids in bone resorption and remodeling.
- Continue
Question 22
22. Identify the cells indicated by the arrows.
Choices:
- osteocytes
- osteocyte
Answers:
- osteocytes
- osteocyte
Comments:
- Correct
- That’s right! Osteocytes are mature bone cells that become surrounded by the matrix they produce.
- Continue
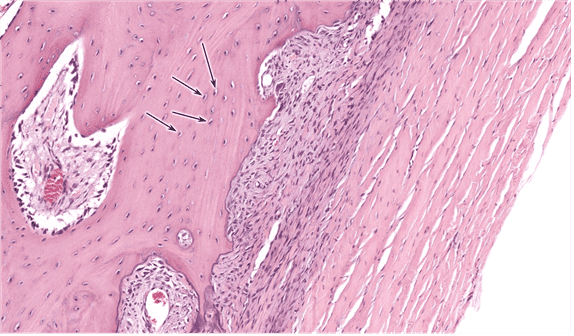
Question 23
23. Identify layer A. Be specific.
Choices:
- cellular layer of periosteum
- deep cellular layer of periosteum
- periosteum, cellular layer
- periosteum, deep cellular layer
- cellular layer, periosteum
- osteogenic layer of periosteum
- periosteum, osteogenic layer
Answers:
- cellular layer of periosteum
- deep cellular layer of periosteum
- periosteum, cellular layer
- periosteum, deep cellular layer
- cellular layer, periosteum
- osteogenic layer of periosteum
- periosteum, osteogenic layer
Comments:
- Correct
- That’s right! The cellular layer of periosteum consists of osteoprogenitor cells, osteoblasts, bone-lining cells and osteoclasts. This layer fxns in bone growth, repair & remodeling.
- Continue
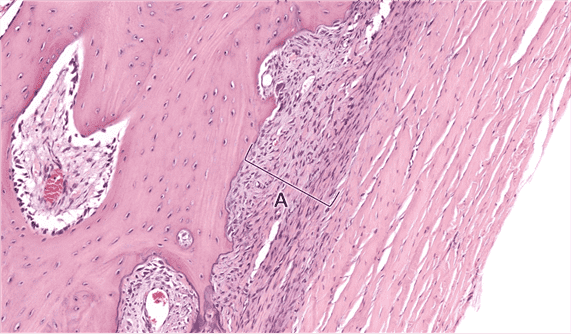
Question 24
24. Identify layer A. Be specific.
Choices:
- fibrous layer of periosteum
- superficial fibrous layer of periosteum
- periosteum, fibrous layer
- periosteum, deep fibrous layer
- fibrous layer, periosteum
- osteogenic layer of periosteum
- periosteum, osteogenic layer
Answers:
- fibrous layer of periosteum
- superficial fibrous layer of periosteum
- periosteum, fibrous layer
- periosteum, deep fibrous layer
- fibrous layer, periosteum
- osteogenic layer of periosteum
- periosteum, osteogenic layer
Comments:
- Correct
- That’s right! The fibrous layer of periosteum is superficial to the cellular layer. This layer is made up of dense irregular CT. It functions in ligament and tendon attachment.
- Continue
Question 25
25. Identify the layer indicated by the arrows.
Choices:
- endosteum
Answers:
- endosteum
Comments:
- Correct
- That’s right! Endosteum lines internal surfaces e.g. marrow cavity, central canal and trabeculae. It is an incomplete layer that fxns in bone growth, repairing and remodeling.
- Continue
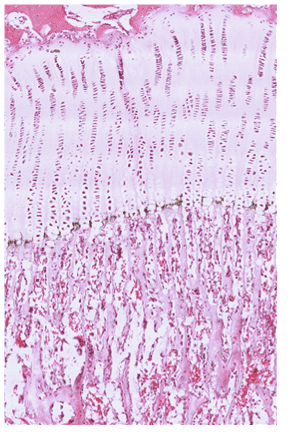
Question 26
26. Identify the structure on the right. Be specific.
Choices:
- epiphyseal plate
- growth plate
- the epiphyseal plate
- the growth plate
- epiphyseal growth plate
- the epiphyseal growth plate
Answers:
- epiphyseal plate
- growth plate
- the epiphyseal plate
- the growth plate
- epiphyseal growth plate
- the epiphyseal growth plate
Comments:
- Correct
- That's right! This is the epiphyseal (growth) plate which separate the diaphysis from the epiphysis. Notice the different zones.
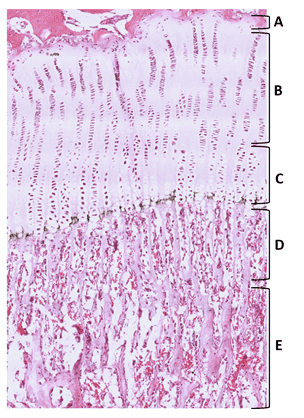
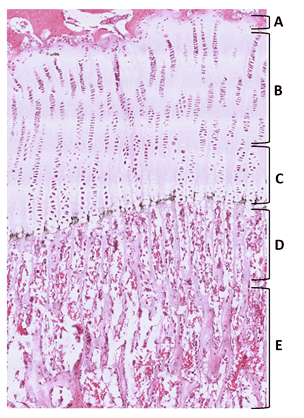
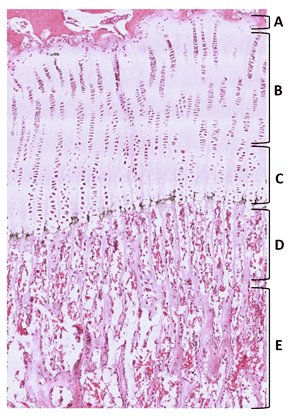
- Continue
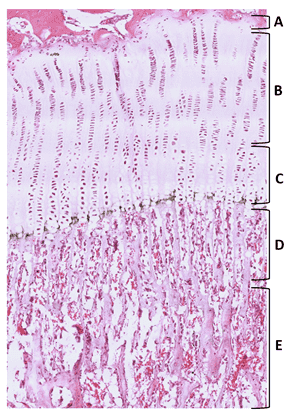
Question 27
27. From the options listed below, identify zone B.
Choices:
- zone of reserve/zone of resting cartilage
- zone of proliferation
- zone of cell maturation and hypertrophy
- zone of calcifying cartilage
- zone of ossification
Answers:
- zone of proliferation
Comments:
- Correct
- That's right! The zone of proliferation contains flattened chondrocytes that stack to form lines.
- Continue
Question 28
28. From the options listed below, identify zone E.
Choices:
- zone of reserve/zone of resting cartilage
- zone of proliferation
- zone of cell maturation and hypertrophy
- zone of calcifying cartilage
- zone of ossification
Answers:
- zone of ossification
Comments:
- Correct
- That's right! The zone of ossification marks bone formation (darker pink stain). BVs from diaphyses penetrate into the calcified cartilage.
- Continue
Question 29
29. From the options listed below, identify zone A.
Choices:
- zone of reserve/zone of resting cartilage
- zone of proliferation
- zone of cell maturation and hypertrophy
- zone of calcifying cartilage
- zone of ossification
Answers:
- zone of reserve/zone of resting cartilage
Comments:
- Correct
- That's right! The zone of reserve/resting cartilage contains chondrocytes that are quiescent and are separate from each other.
- Continue
Question 30
30. From the options listed below, identify zone C.
Choices:
- zone of reserve/zone of resting cartilage
- zone of proliferation
- zone of cell maturation and hypertrophy
- zone of calcifying cartilage
- zone of ossification
Answers:
- zone of cell maturation and hypertrophy
Comments:
- Correct
- That's right! Zone of cell maturation and hypertrophy contains enlarged chondrocytes that are stacked.
- Continue
Question 31
31. From the options listed below, identify zone D.
Choices:
- zone of reserve/zone of resting cartilage
- zone of proliferation
- zone of cell maturation and hypertrophy
- zone of calcifying cartilage
- zone of ossification
Answers:
- zone of calcifying cartilage
Comments:
- Correct
- That's right! Zone of calcifying cartilage contains dead chondrocytes and calcified matrix.
- Continue