Question 1
1. Anatomically, 'thick skin" and "thin skin" refer to differences in the thickness of the:
Choices:
- Papillary layer of the dermis
- Hypodermis
- Epidermis
- Reticular layer of the dermis
Answers:
- Epidermis
Comments:
- Correct
- That’s right! Thick and thin skin refer to the thickness of the epidermis.
- Continue
Question 2
2. From the options listed below, choose the CORRECT statement(s) regarding sebaceous glands.
Choices:
- Their secretory activity increases under hormonal influence at puberty
- They may become blocked, resulting in acne.
- They are distributed over most of the body surface
- They are numerous in thick skin
- The products of sebaceous glands function in thermoregulation
Answers:
- Their secretory activity increases under hormonal influence at puberty
- They may become blocked, resulting in acne.
- They are distributed over most of the body surface
Comments:
- Correct
- That’s right! Sebaceous glands are distributed over most of body surface and are influenced by circulating hormones. Hypersecretion of sebaceous glands can block follicles contributing to acne.
- Continue
Question 3
3. From deep to superficial, order the following structures.
Choices:
- Reticular layer of dermis
- Papillary layer of dermis
- Stratum basale
- Stratum spinosum
- Stratum granulosum
- Stratum corneum
Answers:
- Reticular layer of dermis
- Papillary layer of dermis
- Stratum basale
- Stratum spinosum
- Stratum granulosum
- Stratum corneum
Comments:
- Correct
- That's right! Thin skin layers from deep to superficial: Reticular layer (dermis)–> papillary layer (dermis) –> SB –> SS –> SG –> SC
- Continue
Question 4
4. From the options listed below, choose the CORRECT statement(s) regarding the mammary glands.
Choices:
- Before puberty, mammary glands are structurally similar in boys and girls.
- The suspensory ligaments (”Cooper’s ligaments”) are dense connective tissue structures that support the weight of the breast.
- Lactiferous sinuses are expansions of the lactiferous ducts deep to the areola.
- A single lactiferous duct drains each lobe.
- Lobes of mammary glands are subdivided into lobules.
- Each mammary gland drains via a single opening at the nipple.
- Intralobular terminal ducts connect lobules to the lactiferous duct system.
Answers:
- Before puberty, mammary glands are structurally similar in boys and girls.
- The suspensory ligaments (”Cooper’s ligaments”) are dense connective tissue structures that support the weight of the breast.
- Lactiferous sinuses are expansions of the lactiferous ducts deep to the areola.
- A single lactiferous duct drains each lobe.
- Lobes of mammary glands are subdivided into lobules.
Comments:
- Correct
- That’s right! The mammary glands contain multiple lobes, each subdivided into lobules. Lobes drain into lactiferous ducts then through the lactiferous sinuses to the openings at the nipple. The gland is structurally similar in both sexes before puberty.
- Continue
Question 5
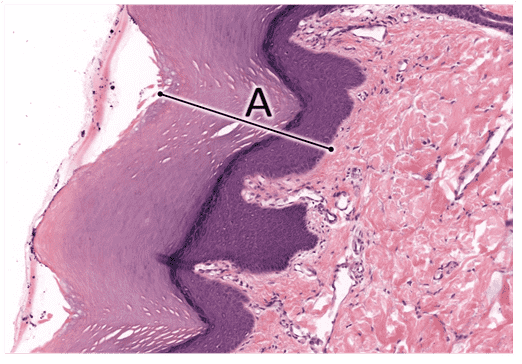
5. Identify the layer of skin indicated by the letter A.
Choices:
- Epidermis
- epidermis
Answers:
- Epidermis
- epidermis
Comments:
- Correct
- That's right! Epidermis is the superficial layer of skin consisting of stratified keratinized squamous epithelium.
- Continue
Question 6
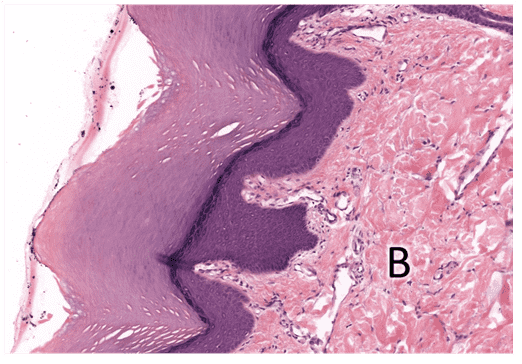
6. Identify the layer of skin indicated by the letter B.
Choices:
- Dermis
- dermis
Answers:
- Dermis
- dermis
Comments:
- Correct
- That's right! Dermis is the CT layer underlying the epidermis. It can be further divided into the papillary and reticular layers.
- Continue
Question 7
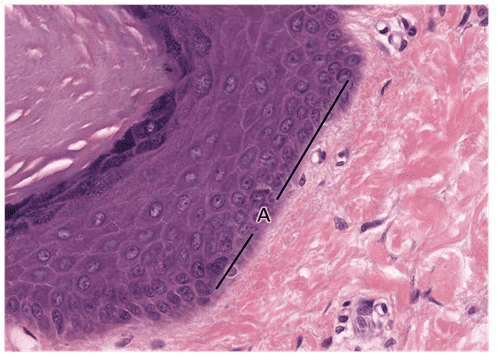
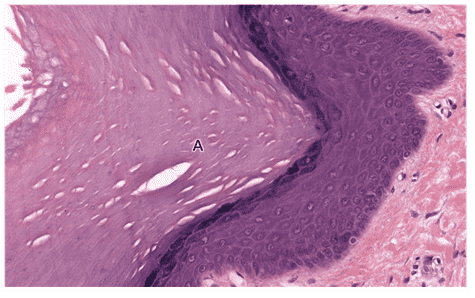
7. Identify the layer indicated by the letter A. Be specific.
Choices:
- Stratum spinosum
- Stratum basale
- Stratum corneum
- Dermis
- Stratum lucidum
- Stratum granulosum
Answers:
- Stratum basale
Comments:
- Correct
- That's right! Stratum basale is the innermost layer of the epidermis. Keratinocytes in this layer undergo rapid cell cycling to maintain skin thickness.
- Continue
Question 8
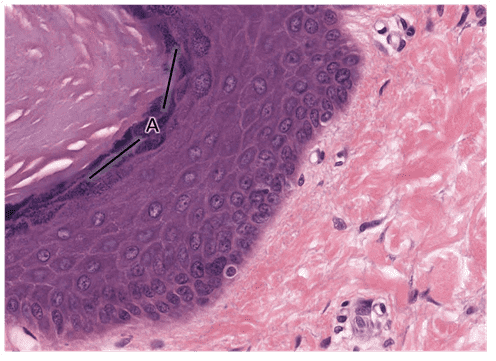
8. Identify the layer indicated by the letter A. Be specific.
Choices:
- Stratum granulosum
- Stratum lucidum
- Stratum basale
- Stratum corneum
- Dermis
Answers:
- Stratum granulosum
Comments:
- Correct
- That's right! Stratum granulosum contains cells undergoing keratinization. Dark-staining keratohyalin granules fill the cytoplasm in this layer.
- Continue
Question 9
9. Identify the layer indicated by the letter A. Be specific.
Choices:
- Stratum basale
- Stratum granulosum
- Stratum corneum
- Stratum lucidum
- Dermis
Answers:
- Stratum corneum
Comments:
- Correct
- That's right! Stratum corneum can be identified by the stratified layer of anucleated squamous cells. Remember, keratinocytes shed their organelles in S. granulosum before entering this layer.
- Continue
Question 10
Identify the layer indicated by the letter A. Be specific.
Choices:
- Stratum basale
- Stratum granulosum
- Stratum spinosum
- Stratum lucidum
- Dermis
Answers:
- Stratum spinosum
Comments:
- Correct
- That's right! Stratum spinosum is the layer between S. granulosum and S. basale. Under high magnification, keratinocytes in this layer appear spiny due to shrinkage of microfilaments between desmosomes.
- Continue
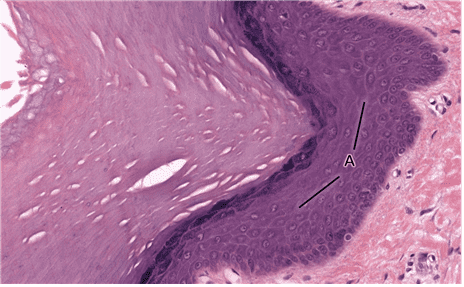
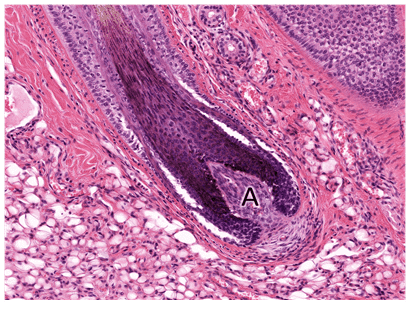
Question 11
11. This structure (A) invaginates into the underlying tissue. What is it called?
Choices:
- epidermal ridge
- Epidermal ridge
- Epidermal ridges
- epidermal ridges
Answers:
- epidermal ridge
- Epidermal ridge
- Epidermal ridges
- epidermal ridges
Comments:
- Correct
- That's right! Epidermal ridges together with the dermal papillae increase SA btw epidermis and dermis for a) enhanced adhesion of layers, b) increased molecular exchange and c) greater number of keratinocytes.
- Continue
Question 12
12. Identify A. Be specific.
Choices:
- Stratum basale
- Reticular layer of dermis
- Elastic layer of dermis
- Papillary layer of dermis
Answers:
- Papillary layer of dermis
Comments:
- Correct
- That's right! The papillary layer of dermis is in contact with the epidermal layer and consists of highly vascularized loose CT.
- Continue
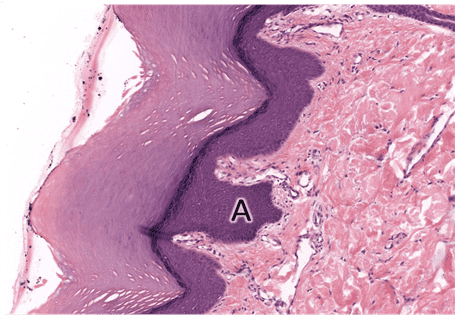
Question 13
13. Identify A. Be specific.
Choices:
- Stratum basale
- Reticular layer of dermis
- Elastic layer of dermis
- Papillary layer of dermis
Answers:
- Reticular layer of dermis
Comments:
- Correct
- That's right! The reticular layer of dermis is made up of dense irregular CT with coarse bundles of collage type I fibres and elastic fibres.
- Continue
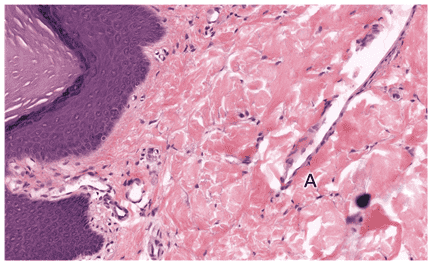
Question 14
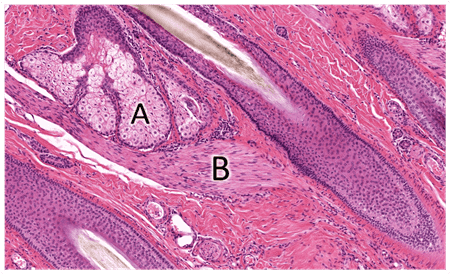
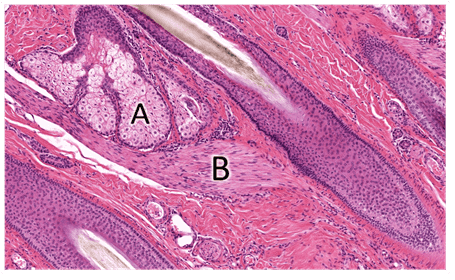
14. Identify A. Be specific.
Choices:
- Apocrine glands
- Eccrine glands
- Sebaceous glands
- Merocrine glands
Answers:
- Sebaceous glands
Comments:
- Correct
- That's right! Sebaceous glands are located near the arrector pilli and open into a hair follicle. Secretory cells containing sebum are characteristic of these glands.
- Continue
Question 15
15. Identify B. Be specific.
Choices:
- Eccrine glands
- Hair bulb
- Sebaceous glands
- Arrector pili muscle
Answers:
- Arrector pili muscle
Comments:
- Correct
- That's right! Arrector pilli is a smooth muscle that fxns in thermoregulation and promotes sebaceous gland secretion upon contraction.
- Continue