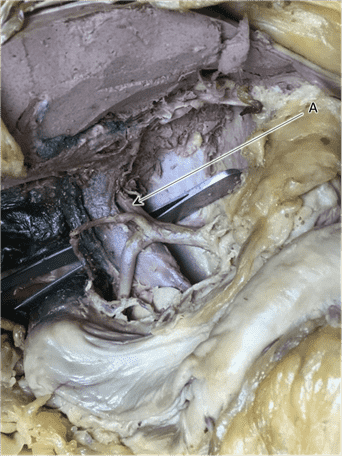
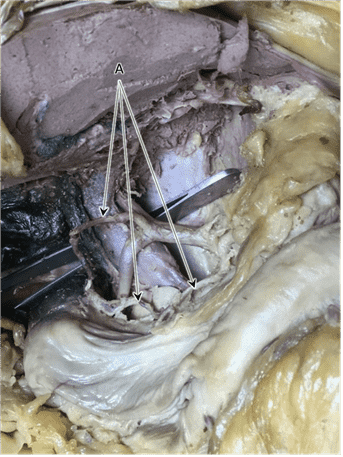
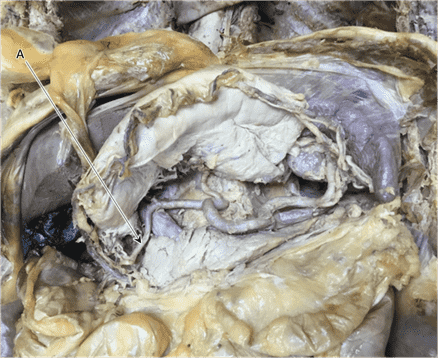
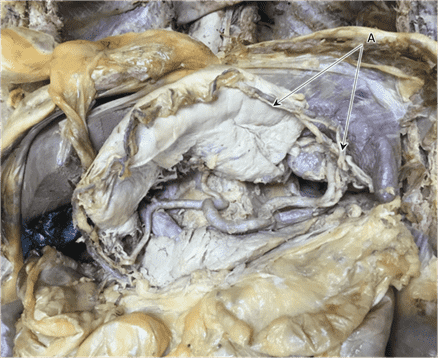
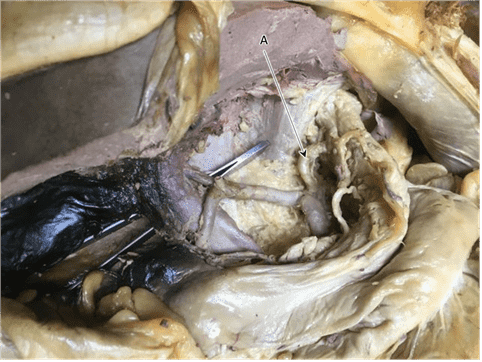
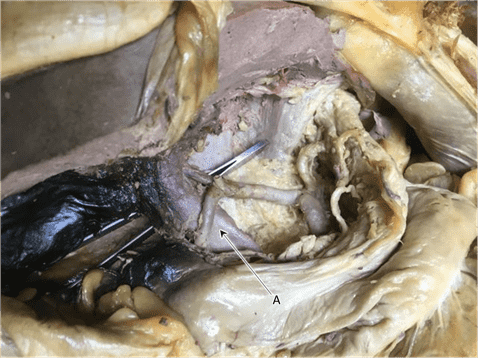
Question 1
1. What term describes the position of an organ that develops within the connective tissue of the posterior abdominal wall?
Choices:
Answers:
Question 2
2. Name the ligament that joins the spleen to the stomach.
Choices:
- gastrosplenic ligament
- the gastrosplenic ligament
- gastrosplenic
Answers:
- gastrosplenic ligament
- the gastrosplenic ligament
- gastrosplenic
Question 3
3. The two subdivisions of the peritoneal cavity are the ___________ and _____________ sacs, the latter also being known as the omental bursa.
Choices:
- greater lesser
- greater, lesser
Answers:
- greater lesser
- greater, lesser
Question 4
4. Which functional subdivision of the nervous system supplies parietal peritoneum with sensory fibres?
Choices:
- somatic
- somatic division
- somatic subdivision
- somatic sensory
- somatic sensory subdivision
- the somatic
- the somatic division
- the somatic sensory subdivision
Answers:
- somatic
- somatic division
- somatic subdivision
- somatic sensory
- somatic sensory subdivision
- the somatic
- the somatic division
- the somatic sensory subdivision
Question 5
5. From which branch of the abdominal aorta does the splenic artery arise?
Choices:
- celiac trunk
- celiac
- celiac artery
- the celiac trunk
- the celiac
- the celiac artery
Answers:
- celiac trunk
- celiac
- celiac artery
- the celiac trunk
- the celiac
- the celiac artery
Question 6
6. Name the ligament that joins the spleen to the posterior body wall.
Choices:
- splenorenal ligament
- the splenorenal ligament
- splenorenal
- the splenorenal
Answers:
- splenorenal ligament
- the splenorenal ligament
- splenorenal
- the splenorenal
Question 7
7. Name the derivative of the dorsal mesentery associated with the greater curvature of the stomach.
Choices:
- the greater omentum
- greater omentum
Answers:
- the greater omentum
- greater omentum
Question 8
8. What term describes the position of an organ that develops within the abdominal cavity and remains suspended in the abdominal cavity attached to the body wall by a mesentery?
Choices:
Answers:
Question 9
9. Which functional subdivision of the nervous system supplies visceral peritoneum with sensory fibres?
Choices:
- autonomic
- autonomic sensory
- autonomic sensory nervous sytem
- the autonomic sensory
- the autonomic sensory nervous system
- the autonomic
- the autonomic subdivision
- autonomic subdivision
Answers:
- autonomic
- autonomic sensory
- autonomic sensory nervous sytem
- the autonomic sensory
- the autonomic sensory nervous system
- the autonomic
- the autonomic subdivision
- autonomic subdivision
Question 10
10. From which branch of the abdominal aorta do the arteries that supply the sigmoid colon arise?
Choices:
- the inferior mesenteric artery
- inferior mesenteric artery
- the inferior mesenteric
- inferior mesenteric
Answers:
- the inferior mesenteric artery
- inferior mesenteric artery
- the inferior mesenteric
- inferior mesenteric
Question 11
11. Which abdominal organ(s) develop(s) wholly within the ventral mesentery? Choose all that apply.
Choices:
- gall bladder
- liver
- stomach
- pancreas
- spleen
Answers:
Question 12
12. What term describes the position of an organ that develops initially within the abdominal cavity, attached to the body wall by a mesentery, but that ultimately becomes fixed to the posterior body wall?
Choices:
- secondarily retroperitoneal
Answers:
- secondarily retroperitoneal
Question 13
13. From which branch of the abdominal aorta do the arteries that supply the cecum arise?
Choices:
- superior mesenteric artery
- the superior mesenteric artery
- the superior mesenteric
- superior mesenteric
Answers:
- superior mesenteric artery
- the superior mesenteric artery
- the superior mesenteric
- superior mesenteric
Question 14
14. Name the one organ that develops wholly within the dorsal mesentery.
Choices:
Answers:
Question 15
15. Name the opening between the greater and lesser sacs.
Choices:
- the epiploic foramen
- epiploic foramen
- the omental foramen
- omental foramen
Answers:
- the epiploic foramen
- epiploic foramen
- the omental foramen
- omental foramen
Question 16
16. Name the organ that develops from two separate embryonic structures, one in the dorsal mesentery and one in the ventral mesentery.
Choices:
Answers:
Question 1
1. Name the ligamentous remnant of the ventral mesentery that contains the right and left gastric arteries.
Choices:
- lesser omentum
- the lesser omentum
Answers:
- lesser omentum
- the lesser omentum
Question 2
2. Name the ligament that joins the spleen to the stomach.
Choices:
- gastrosplenic ligament
- the gastrosplenic ligament
- gastrosplenic
Answers:
- gastrosplenic ligament
- the gastrosplenic ligament
- gastrosplenic
Question 3
3. Name the vein that runs in the hepatoduodenal ligament.
Choices:
- hepatic portal vein
- hepatic portal
- the hepatic portal vein
Answers:
- hepatic portal vein
- hepatic portal
- the hepatic portal vein
Question 4
4. Name the ligament that joins the spleen to the posterior body wall.
Choices:
- splenorenal
- the splenorenal
- the splenorenal ligament
- splenorenal ligament
Answers:
- splenorenal
- the splenorenal
- the splenorenal ligament
- splenorenal ligament
Question 5
5. From what branch of the abdominal aorta does the splenic artery arise?
Choices:
- celiac trunk
- celiac
- celiac artery
- the celiac trunk
- the celiac
- the celiac artery
Answers:
- celiac trunk
- celiac
- celiac artery
- the celiac trunk
- the celiac
- the celiac artery
Question 6
6. Name the two portions of the small intestine that are intraperitoneal.
Choices:
- jejunum and ileum
- jejunum, ileum
- ileum and jejunum
- ileum, jejunum
- the jejunum and ileum
- the jejunum, ileum
- the ileum, jejunum
- the ileum and jejunum
- ileum jejunum
- jejunum ileum
Answers:
- jejunum and ileum
- jejunum, ileum
- ileum and jejunum
- ileum, jejunum
- the jejunum and ileum
- the jejunum, ileum
- the ileum, jejunum
- the ileum and jejunum
- ileum jejunum
- jejunum ileum
Question 7
7. Name the artery that runs within the hepatoduodenal ligament.
Choices:
- hepatic artery proper
- the hepatic artery proper
Answers:
- hepatic artery proper
- the hepatic artery proper
Question 8
8. Besides the hepatic portal vein and the hepatic artery proper, what third structure is located in the hepatoduodenal ligament?
Choices:
- common bile duct
- the common bile duct
Answers:
- common bile duct
- the common bile duct
Question 9
9. What artery runs in the splenorenal ligament?
Choices:
- splenic
- the splenic
- the splenic artery
- splenic artery
Answers:
- splenic
- the splenic
- the splenic artery
- splenic artery
Question 10
10. Which arteries run in the greater omentum along its line of attachment to the greater curvature of the stomach? Choose all that apply.
Choices:
- the left gastro-omental (gastroepiploic) artery
- the right gastro-omental (gastroepiploic) artery
- the celiac artery
- the hepatic artery proper
- the splenic artery
- the short gastric arteries
- the left gastric artery
- the right gastric artery
Answers:
- the left gastro-omental (gastroepiploic) artery
- the right gastro-omental (gastroepiploic) artery
Question 11
11. Name the ligament that attaches the liver to the diaphragm and anterior body wall.
Choices:
- falciform
- the falciform
- the falciform ligament
- falciform ligament
Answers:
- falciform
- the falciform
- the falciform ligament
- falciform ligament
Question 12
12. Name the subdivision of the lesser omentum that stretches between the lesser curvature of the stomach and the liver.
Choices:
- hepatogastric ligament
- the hepatogastric ligament
Answers:
- hepatogastric ligament
- the hepatogastric ligament
Question 13
13. In what quadrant of the abdomen is the spleen located?
Choices:
- left upper
- upper left
- the left upper
- the upper left
- left upper quadrant
- upper left quadrant
- the left upper quadrant
- the upper left quadrant
Answers:
- left upper
- upper left
- the left upper
- the upper left
- left upper quadrant
- upper left quadrant
- the left upper quadrant
- the upper left quadrant
Question 14
14. Name the opening between the greater and lesser sacs.
Choices:
- the epiploic foramen
- epiploic foramen
- omental foramen
- the omental foramen
Answers:
- the epiploic foramen
- epiploic foramen
- omental foramen
- the omental foramen
Question 15
15. From proximal to distal, the two parts of the large intestine that are secondarily retroperitoneal are the _____________ and _____________ colon.
Choices:
Answers:
Question 16
16. The ____________ ligaments run from left to right across the superior surface of the liver and attach it to the diaphragm.
Choices:
Answers:
Question 17
17. The mesentery contains the arteries that supply the jejunum and ileum. From what branch of the aorta do these arteries arise?
Choices:
- superior mesenteric
- the superior mesenteric
- the superior mesenteric artery
- superior mesenteric artery
Answers:
- superior mesenteric
- the superior mesenteric
- the superior mesenteric artery
- superior mesenteric artery
Question 18
18. If you pass your finger into the epiploic foramen, what major vessel is posterior to your finger?
Choices:
- the inferior vena cava
- inferior vena cava
Answers:
- the inferior vena cava
- inferior vena cava
Question 19
19. In what quadrant of the abdomen is the cecum located?
Choices:
- the right lower quadrant
- right lower quadrant
- right lower
- the lower right quadrant
- lower right quadrant
- lower right
Answers:
- the right lower quadrant
- right lower quadrant
- right lower
- the lower right quadrant
- lower right quadrant
- lower right
Question 20
20. The ________ _________ is located in the free inferior border of the falciform ligament.
Choices:
Answers:
Question 21
21. What two ligaments form the left lateral border of the lesser sac?
Choices:
- the splenorenal ligament and the gastrosplenic ligament
- splenorenal ligament and gastrosplenic ligament
- splenorenal and gastrosplenic ligaments
- the gastrosplenic ligament and the splenorenal ligament
- gastrosplenic ligament and splenorenal ligament
- gastrosplenic and splenorenal ligaments
- splenorenal and gastrosplenic
- gastrosplenic and splenorenal
- splenorenal gastrosplenic
- gastrosplenic splenorenal
Answers:
- the splenorenal ligament and the gastrosplenic ligament
- splenorenal ligament and gastrosplenic ligament
- splenorenal and gastrosplenic ligaments
- the gastrosplenic ligament and the splenorenal ligament
- gastrosplenic ligament and splenorenal ligament
- gastrosplenic and splenorenal ligaments
- splenorenal and gastrosplenic
- gastrosplenic and splenorenal
- splenorenal gastrosplenic
- gastrosplenic splenorenal