Question 1
1. The region anterior to the elbow is the ___________ ___________.
Choices:
- cubital fossa
Answers:
- cubital fossa
Comments:
- Correct
- That's right! The cubital fossa is located anterior to the elbow. It is one of the transitional zones of the upper limb.
- Continue
Question 2
2. The region anterior to the wrist, through which tendons pass from the forearm to the hand is called the ________________ ___________________.
Choices:
- carpal tunnel
Answers:
- carpal tunnel
Comments:
- Correct
- That's right! The carpal tunnel is located anterior to the wrist (radiocarpal joint). This region is bordered by carpal bones and flexor retinaculum.
- Continue
Question 3
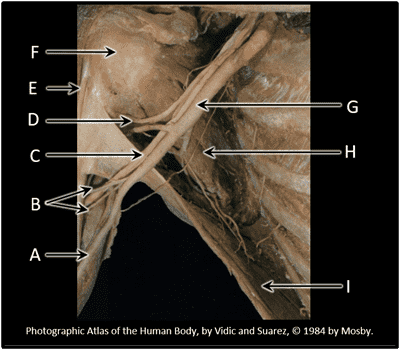
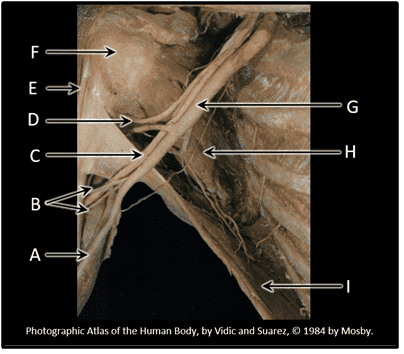
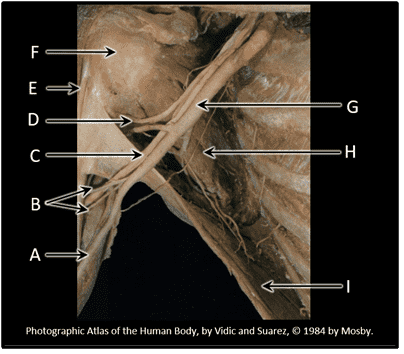
3. Neurovascular structures that pass between the neck or thorax and the upper limb must pass through the region known as the _________________.
Choices:
- axilla
Answers:
- axilla
Comments:
- Correct
- That's right! Major neurovascular structures from neck/thorax must pass through the axilla to reach upper limb.
- Continue
Question 4
4. Which of the following functional subtypes of neurons is found in a peripheral nerve innervating the body wall or limbs? Choose all that apply.
Choices:
- postganglionic sympathetic
- somatic motor
- sensory
- postganglionic parasympathetic
- preganglionic parasympathetic
- preganglionic sympathetic
Answers:
- postganglionic sympathetic
- somatic motor
- sensory
Comments:
- Correct
- That's right! Peripheral nerves that innervate the body wall/limbs contain somatic sensory, motor and postganglionic sympathetic fibres.
- Continue
Question 5
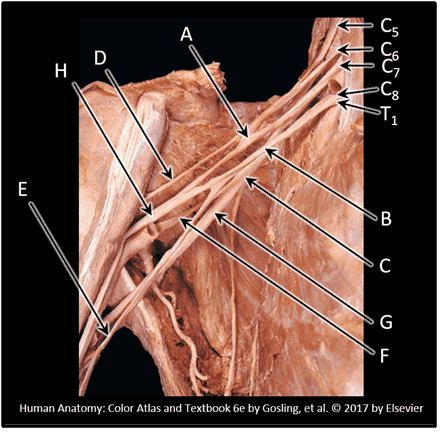
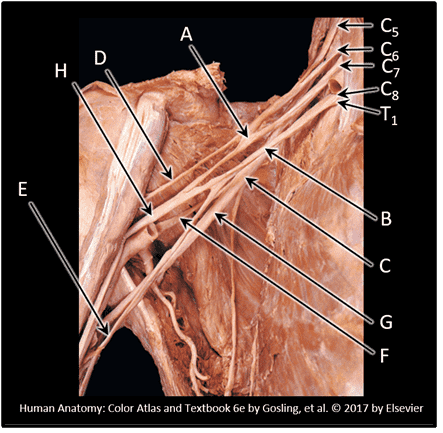
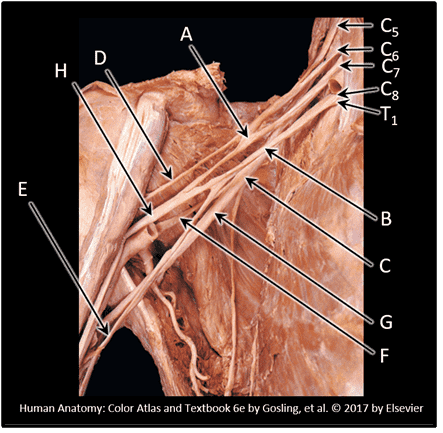
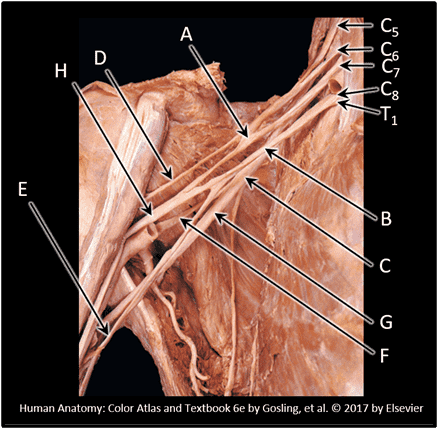
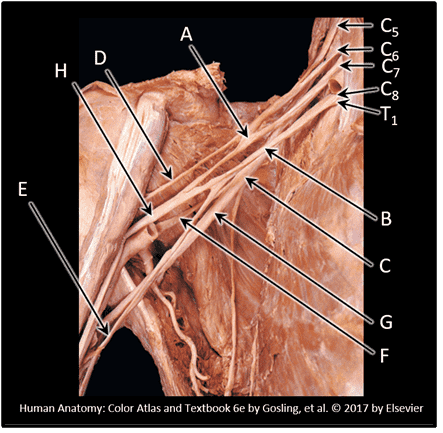
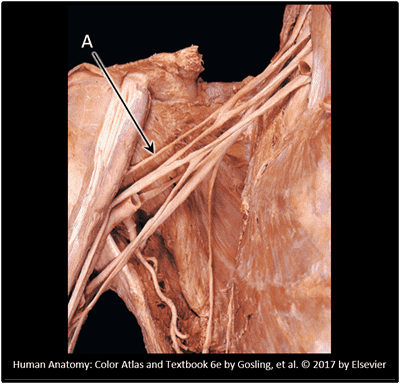
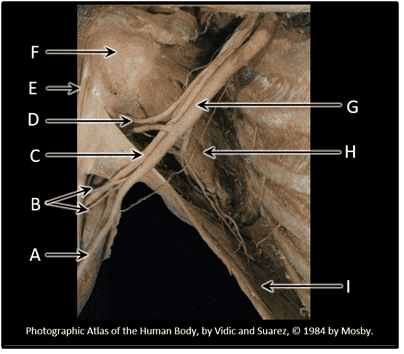
5. Which spinal levels contribute to the formation of the brachial plexus? Choose all that apply.
Choices:
- T1
- C8
- C7
- C6
- C5
- T3
- T2
- C4
- C3
Answers:
- T1
- C8
- C7
- C6
- C5
Comments:
- Correct
- That's right! The brachial plexus forms from the ventral rami of 5 spinal nerves, C5 - T1. Remember, although there is a C8 spinal nerve, there is NO C8 vertebra!
- Continue
Question 6
6. The subclavian artery continues distally as the ________________ artery.
Choices:
- axillary
Answers:
- axillary
Comments:
- Correct
- That's right! When the subclavian artery enters the axilla, it becomes the axillary artery.
- Continue
Question 7
7. The axillary vein continues proximally as the _________________ vein.
Choices:
- subclavian
Answers:
- subclavian
Comments:
- Correct
- That's right! The axillary vein continues as the subclavian vein to drain blood away from upper limb.
- Continue
Question 8
8. A _______________ nerve contains fibres from multiple spinal levels.
Choices:
- compound
Answers:
- compound
Comments:
- Correct
- That's right! Compound nerves contain fibres from multiple spinal levels.
- Continue
Question 9
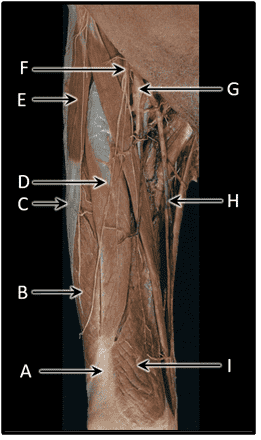
9. What are the key characteristics of the musculocutaneous nerve in the arm? Choose all that apply.
Choices:
- It controls flexion of the elbow.
- It innervates the muscles of the anterior compartment of the arm.
- It controls abduction of the glenohumeral joint.
- It innervates the deltoid muscle.
- It controls extension of the elbow.
- It innervates the muscles of the posterior compartment of the arm.
Answers:
- It controls flexion of the elbow.
- It innervates the muscles of the anterior compartment of the arm.
Comments:
- Correct
- That's right! The musculocutaneous nerve innervates muscles of the anterior compartment of the arm, which are responsible for flexion of the elbow.
- Continue
Question 10
10. What are the key characteristics of the radial nerve in the arm? Choose all that apply.
Choices:
- It controls extension of the elbow.
- It innervates the muscles of the posterior compartment of the arm.
- It controls abduction of the glenohumeral joint.
- It innervates the deltoid muscle.
- It controls flexion of the elbow.
- It innervates the muscles of the anterior compartment of the arm.
Answers:
- It controls extension of the elbow.
- It innervates the muscles of the posterior compartment of the arm.
Comments:
- Correct
- That's right! The radial nerve innervates muscles of the posterior compartment of arm, therefore it controls extension of elbow.
- Continue
Question 11
11. What are the key characteristics of the axillary nerve? Choose all that apply.
Choices:
- It controls abduction of the glenohumeral joint.
- It innervates the deltoid muscle.
- It controls extension of the elbow.
- It controls flexion of the elbow.
- It innervates the muscles of the posterior compartment of the arm.
- It innervates the muscles of the anterior compartment of the arm.
Answers:
- It controls abduction of the glenohumeral joint.
- It innervates the deltoid muscle.
Comments:
- Correct
- That's right! The axillary nerve innervates the deltoid muscle, which is a major abductor of the glenohumeral joint.
- Continue
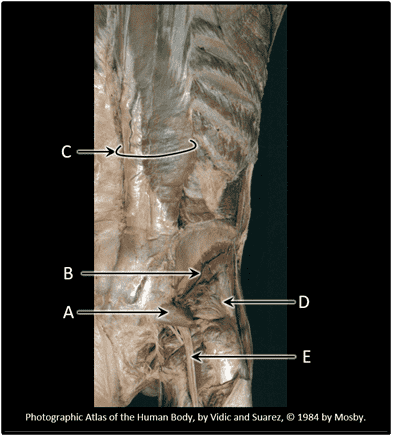
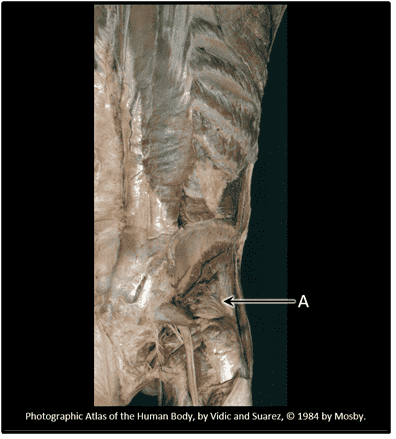
Question 12
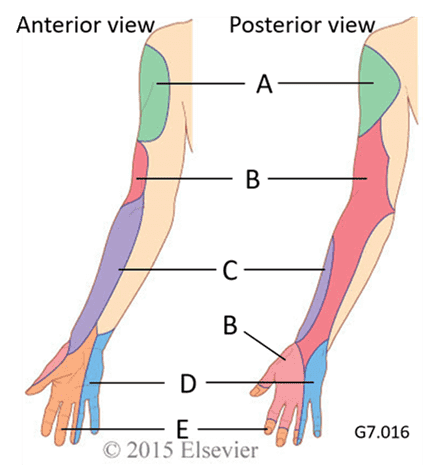
12. What is the cutaneous distribution of the radial nerve?
Choices:
- A
- B
- C
- D
- E
Answers:
- B
Comments:
- Correct
- That's right! The radial nerve contains sensory fibres that are responsible for monitoring the skin of the posterior arm, forearm and lateral hand (B).
- Continue
Question 13
13. What is the cutaneous distribution of the ulnar nerve?
Choices:
- A
- B
- C
- D
- E
Answers:
- D
Comments:
- Correct
- That's right! The ulnar nerve innervates the medial hand and one-and-a-half digits (D).
- Continue
Question 14
14. What is the cutaneous distribution of the median nerve?
Choices:
- A
- B
- C
- D
- E
Answers:
- E
Comments:
- Correct
- That's right! The median nerve provides sensory input from the skin of the palmar surface of the hand and lateral three and a half digits (E).
- Continue
Question 15
15. What is the cutaneous distribution of the axillary nerve?
Choices:
- A
- B
- C
- D
- E
Answers:
- A
Comments:
- Correct
- That's right! The axillary nerve monitors skin on the lateral aspect of the shoulder (A).
- Continue
Question 16
16. What is the cutaneous distribution of the musculocutaneous nerve?
Choices:
- A
- B
- C
- D
- E
Answers:
- C
Comments:
- Correct
- That's right! The musculocutaneous nerve monitors the skin of the lateral forearm (C).
- Continue
Question 17
17. A _____ nerve contains both sensory and motor fibres.
Choices:
- mixed
Answers:
- mixed
Comments:
- Correct
- That's right! A mixed nerve contains both sensory and motor fibres, therefore when lesioned it can cause both motor and sensory deficits.
- Continue
Question 18
18. The _________________ nerve is most closely associated with the surgical neck of the humerus.
Choices:
- axillary
Answers:
- axillary
Comments:
- Correct
- That's right! The axillary nerve is closely associated with the surgical neck of the humerus, therefore injury to the area may lead to nerve damage.
- Continue
Question 19
19. The _________________ nerve is most closely associated with the medial epicondyle of the humerus.
Choices:
- ulnar
Answers:
- ulnar
Comments:
- Correct
- That's right! The ulnar nerve passes posterior to the medial epicondyle of the humerus where it is vulnerable to fracture or compression.
- Continue
Question 20
20. The _________________ nerve is most closely associated with the spiral groove of the humerus.
Choices:
- radial
Answers:
- radial
Comments:
- Correct
- That's right! The radial nerve runs obliquely across the spiral groove of the humerus and is therefore vulnerable to fracture of its midshaft.
- Continue
Question 21
21. The region posterior to the knee is known as the ___________ ____________.
Choices:
- popliteal fossa
Answers:
- popliteal fossa
Comments:
- Correct
- That's right! The popliteal fossa is located posterior to the knee. It connects the posterior thigh and the leg. It is a transitional zone of the lower limb.
- Continue
Question 22
22. Which spinal levels contribute to the lumbar plexus? Choose all that apply.
Choices:
- L4
- L3
- L2
- L1
- S2
- S1
- L5
- T12
Answers:
- L4
- L3
- L2
- L1
Comments:
- Correct
- That's right! The lumbar plexus forms in the posterior abdominal wall, from the ventral rami of spinal nerves from L1 to L4.
- Continue
Question 23
23. Which spinal levels contribute to the sacral plexus? Choose all that apply.
Choices:
- S4
- S3
- S2
- S1
- L5
- L4
- Co1
- S5
Answers:
- S4
- S3
- S2
- S1
- L5
- L4
Comments:
- Correct
- That's right! The sacral plexus contain ventral rami from L4 to S4 spinal levels. It forms in the pelvis, and together with the lumbar plexus, give rise to peripheral nerves that innervate the lower limb, abdominal wall and perineum.
- Continue
Question 24
24. The external iliac artery continues distally as the ___________ artery.
Choices:
- femoral
Answers:
- femoral
Comments:
- Correct
- That's right! When the external iliac artery passes under the inguinal ligament, it becomes the femoral artery.
- Continue
Question 25
25. What are the key characteristics of the femoral nerve in the thigh? Choose all that apply.
Choices:
- It innervates the quadriceps muscle.
- It controls extension of the knee.
- It innervates the muscles of the anterior compartment of the thigh.
- It innervates the hamstrings muscles.
- It controls adduction of the hip.
- It controls flexion of the knee.
- It innervates the muscles of the medial compartment of the thigh.
- It innervates the muscles of the posterior compartment of the thigh.
Answers:
- It innervates the quadriceps muscle.
- It controls extension of the knee.
- It innervates the muscles of the anterior compartment of the thigh.
Comments:
- Correct
- That's right! The femoral nerve innervates the muscles of the anterior compartment of thigh, such as the quadriceps. These muscles are responsible for extension of knee.
- Continue
Question 26
26. What are the key characteristics of the obturator nerve in the thigh? Choose all that apply.
Choices:
- It controls adduction of the hip.
- It innervates the muscles of the medial compartment of the thigh.
- It innervates the hamstrings muscles.
- It innervates the quadriceps muscle.
- It controls extension of the knee.
- It controls flexion of the knee.
- It innervates the muscles of the posterior compartment of the thigh.
- It innervates the muscles of the anterior compartment of the thigh.
Answers:
- It controls adduction of the hip.
- It innervates the muscles of the medial compartment of the thigh.
Comments:
- Correct
- That's right! The obturator nerve innervates (most of) the muscles of the medial compartment of the thigh, which are responsible for adduction of hip.
- Continue
Question 27
27. What are the key characteristics of the sciatic nerve in the thigh? Choose all that apply.
Choices:
- It innervates the hamstrings muscles.
- It controls flexion of the knee.
- It innervates the muscles of the posterior compartment of the thigh.
- It innervates the quadriceps muscle.
- It controls adduction of the hip.
- It controls extension of the knee.
- It innervates the muscles of the medial compartment of the thigh.
- It innervates the muscles of the anterior compartment of the thigh.
Answers:
- It innervates the hamstrings muscles.
- It controls flexion of the knee.
- It innervates the muscles of the posterior compartment of the thigh.
Comments:
- Correct
- That's right! The sciatic nerve innervates muscles of the posterior compartment of the thigh, the hamstrings. These muscles are responsible for flexion of the knee.
- Continue
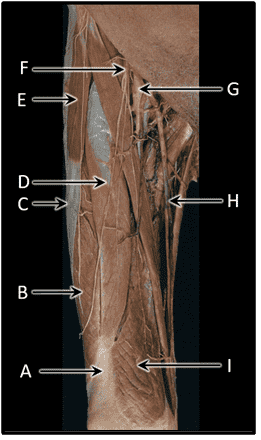
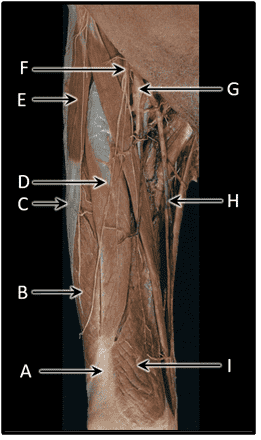
Question 28
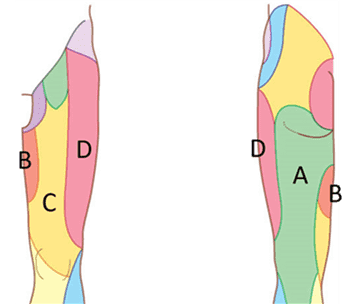
28. What is the cutaneous distribution of the femoral nerve?
Choices:
- A
- B
- C
- D
Answers:
- C
Comments:
- Correct
- That's right! The femoral nerve monitors the skin of the anterior thigh (C).
- Continue
Question 29
29. What is the cutaneous distribution of the posterior cutaneous nerve of the thigh?
Choices:
- A
- B
- C
- D
Answers:
- A
Comments:
- Correct
- That's right! The posterior cutaneous nerve of the thigh monitors the skin of the posterior thigh (A).
- Continue
Question 30
30. What is the cutaneous distribution of the obturator nerve?
Choices:
- A
- B
- C
- D
Answers:
- B
Comments:
- Correct
- That's right! The obturator nerve monitors skin of the medial thigh (B).
- Continue
Question 31
31. What is the cutaneous distribution of the lateral cutaneous nerve of the thigh?
Choices:
- A
- B
- C
- D
Answers:
- D
Comments:
- Correct
- That's right! The lateral cutaneous nerve of the thigh monitors the skin of the lateral thigh (D).
- Continue
Question 32
32. The femoral nerve arises from the _____________ plexus.
Choices:
- lumbar
Answers:
- lumbar
Comments:
- Correct
- That's right! The femoral nerve arises from the lumbar plexus.
- Continue
Question 33
33. The posterior cutaneous nerve of the thigh arises from the ___________ plexus.
Choices:
- sacral
Answers:
- sacral
Comments:
- Correct
- That's right! The posterior cutaneous nerve of thigh arises from the sacral plexus.
- Continue
Question 34
34. The sciatic nerve arises from the ___________ plexus.
Choices:
- sacral
Answers:
- sacral
Comments:
- Correct
- That's right! The sciatic nerve arises from the sacral plexus.
- Continue
Question 35
35. The obturator nerve arises from the _____________ plexus.
Choices:
- lumbar
Answers:
- lumbar
Comments:
- Correct
- That's right! The obturator nerve arises from the lumbar plexus.
- Continue
Question 36
36. The lateral cutaneous nerve of the thigh arises from the _____________ plexus.
Choices:
- lumbar
Answers:
- lumbar
Comments:
- Correct
- That's right! The lateral cutaneous nerve of thigh arises from the lumbar plexus.
- Continue