Question 1
1. In a lower motor neuron lesion, reflexes are ______________.
Choices:
- decreased
- normal
- increased
Answers:
Question 2
2. In an upper motor neuron lesion, reflexes are ______________.
Choices:
- decreased
- normal
- increased
Answers:
Question 3
3. In a lower motor neuron lesion, muscle tone is ______________.
Choices:
- decreased
- normal
- increased
Answers:
Question 4
4. In an upper motor neuron lesion, firm stroking of the sole of the foot causes ___________ of the ankle and ________ and ______________ of the toes.
(3 answers; separate with 1 space each)
Choices:
- dorsiflexion extension spreading
- dorsiflexion spreading extension
Answers:
- dorsiflexion extension spreading
- dorsiflexion spreading extension
Question 5
5. The patellar reflex tests the ________ spinal level.
Choices:
Answers:
Question 6
6. Lesions of a spinal nerve, or its branches, always have ipsilateral effects.
Choices:
Answers:
Question 8
8. The biceps reflex tests the ________ spinal level.
Choices:
Answers:
Question 9
9. In a lower motor neuron lesion, muscle atrophy is ______________.
Choices:
- marked
- mild, only seen with time
- not seen
Answers:
Question 10
10. Lesion of a cranial nerve always has ipsilateral effects.
Choices:
Answers:
Question 11
11. In an upper motor neuron lesion, muscle tone is ______________.
Choices:
- decreased
- normal
- increased
Answers:
Question 12
12. Lesions of a spinal nerve, or its peripheral branches, _________ have ipsilateral effects.
Choices:
- always
- usually
- sometimes
- never
Answers:
Question 13
13. Lesions of a cranial nerve nucleus containing lower motor neurons _________ has ipsilateral effects.
Choices:
- always
- usually
- sometimes
- never
Answers:
Question 14
14. Lesions of ventral horn cells of the spinal cord _________ have ipsilateral effects.
Choices:
- always
- usually
- sometimes
- never
Answers:
Question 15
15. The only cranial nerve nucleus, the lesion of which causes contralateral effects, is the ____________ nucleus.
Choices:
Answers:
Question 16
16. Which of the following structures contain upper motor neurons? Choose all that apply:
Choices:
- lateral column of spinal cord white matter
- pyramids
- internal capsule
- cerebral peduncles
- spinal nerves
- cranial nerves
- cerebellar peduncles
Answers:
- lateral column of spinal cord white matter
- pyramids
- internal capsule
- cerebral peduncles
Question 17
17. Normally, firm stroking of the sole of the foot causes ______________ of the ankle and ____________ of the toes. (2 answers; separate with 1 space)
Choices:
Answers:
Question 18
18. The triceps reflex tests the ________ spinal level.
Choices:
Answers:
Question 19
19. In an upper motor neuron lesion, muscle atrophy is ______________.
Choices:
- marked
- mild, only seen with time
- not seen
Answers:
- mild, only seen with time
Question 20
20. Lesions of upper motor neurons to the body in the brainstem or higher _____________ have contralateral effects.
Choices:
- always
- usually
- sometimes
- never
Answers:
Question 21
21. The achilles reflex tests the ________ spinal level.
Choices:
Answers:
Question 1
1. General sensation from the body is perceived in primary somatosensory cortex, located in the _________________ gyrus.
Choices:
Answers:
Question 2
2. The dorsal horn of the spinal cord is for the body what the _______________ __________ nucleus is for the face.
Choices:
Answers:
Question 3
3. Light touch, vibration and conscious proprioception are localized to the _________ __________ of spinal white matter. (separate answers with 1 space)
Choices:
Answers:
Question 4
4. Somatotopy in the dorsal columns is such that sensations from more caudal dermatomes is _________________ to those from more rostral dermatomes.
Choices:
Answers:
Question 5
5. Sensations of fine touch, vibration and conscious proprioception from the lower body travel in the _________________ _______________ of the spinal cord dorsal columns. (separate answers with one space)
Choices:
Answers:
Question 6
6. The chief sensory nucleus of the trigeminal nerve is for the face as the nucleus ______________ and nucleus ___________ are for the body. (2 answers; separate with 1 space)
Choices:
- gracilis cuneatus
- cuneatus gracilis
Answers:
- gracilis cuneatus
- cuneatus gracilis
Question 7
7. All modalities of general sensation from the body and face relay through the _____________ ______________ nucleus of the thalamus.
Choices:
Answers:
Question 7
7. Lesions of upper motor neurons in the spinal cord _____________ have ipsilateral effects.
Choices:
- always
- usually
- sometimes
- never
Answers:
Question 8
8. The fasciculus _____________ is present throughout the length of the spinal cord dorsal columns, while the fasciculus _____________ is only present at upper thoracic and cervical levels. (2 answers; separate with 1 space)
Choices:
- gracilis cuneatus
- cuneatus gracilis
Answers:
- gracilis cuneatus
- cuneatus gracilis
Question 9
9. Axons of the trigeminal nerve carrying nociception and temperature sensations from the face synapse on neurons in the _________________ _________________ nucleus.
Choices:
Answers:
Question 10
10. Dorsal root ganglia are for the body what the _______________ ganglion is for the face.
Choices:
Answers:
Question 11
11. Sensations of fine touch, vibration and conscious proprioception from the upper body travel in the _________________ _______________ of the spinal cord dorsal columns. (2 words separated by 1 space)
Choices:
Answers:
Question 12
12. The nucleus cuneatus receives sensations of fine touch, vibration and conscious proprioception sensations from the _______________ side of the body.
Choices:
- contralateral
- ipsilateral
Answers:
Question 13
13. Within the dorsal columns of the spinal cord, the fasciculus gracilis is _______________ to the fasciculus cuneatus.
Choices:
Answers:
Question 14
14. The spinal cord dorsal columns carry sensations of fine touch, vibration and conscious proprioception sensations from the _______________ side of the body.
Choices:
- contralateral
- ipsilateral
Answers:
Question 15
15. The spinothalamic tract caries nociception and temperature sensations from the _______________ side of the body.
Choices:
- contralateral
- ipsilateral
Answers:
Question 16
16. Dorsal horn cells receive input from the body and limbs regarding two somatosensory modalities, __________________ and _________________.
Choices:
- nociception temperature
- temperature nociception
Answers:
- nociception temperature
- temperature nociception
Question 17
17. The nucleus gracilis receives sensations of fine touch, vibration and conscious proprioception sensations from the _______________ side of the body.
Choices:
- contralateral
- ipsilateral
Answers:
Question 1
1. The two cranial nerve nuclei at the level of the caudal pons that contain lower
motor neurons are the _____________ nucleus and the _____________ nucleus. (separate answer by one space)
Choices:
- abducens facial
- facial abducens
Answers:
- abducens facial
- facial abducens
Question 2
2. Axons and neurons coding for nociception and temperature from the face are located throughout the ______________.
Choices:
Answers:
Question 3
3. Throughout the pons, the corticospinal tract is located ______________ to cranial nerve nuclei.
Choices:
Answers:
Question 4
4. The _________ (cranial nerve) nucleus is located at the rostral midbrain.
Choices:
Answers:
Question 5
5. At the level of the open medulla, the __________________nucleus is located most medially.
Choices:
Answers:
Question 6
6. Nuclei of three cranial nerves are located ____________ to the corticospinal tract at the level of the caudal pons.
Choices:
Answers:
Question 7
7. The ____________ nucleus of the trigeminal nerve and the __________ nucleus of the trigeminal nerve are located at the level of the mid pons. (2 answers separated by one space)
Choices:
- motor main
- main motor
- motor chief
- chief motor
- chief sensory motor
- motor chief sensory
Answers:
- motor main
- main motor
- motor chief
- chief motor
- chief sensory motor
- motor chief sensory
Question 8
8. The corticospinal tracts are located in the ___________ aspect of the medulla.
Choices:
Answers:
Question 1
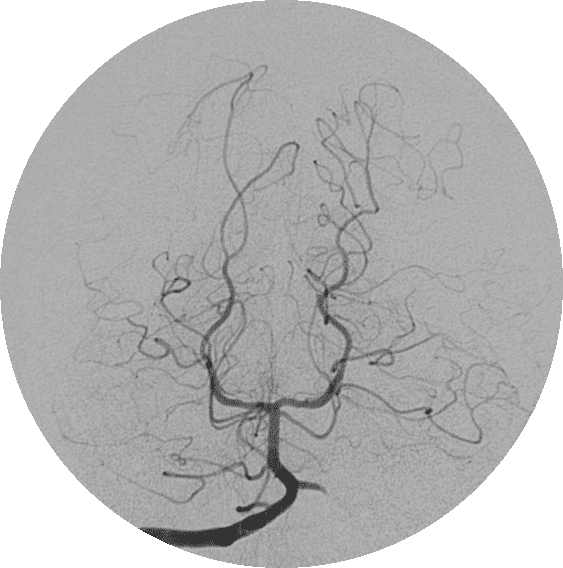
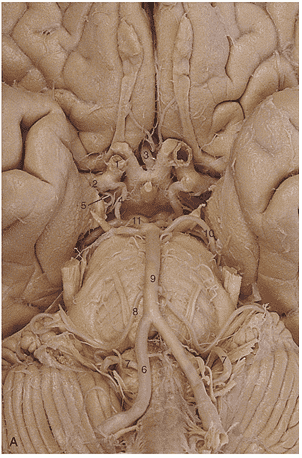
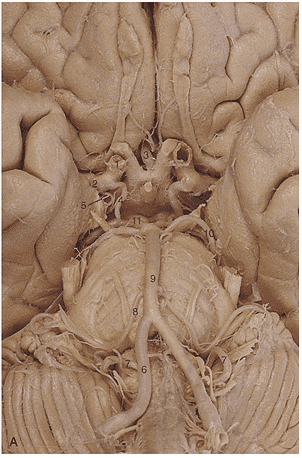
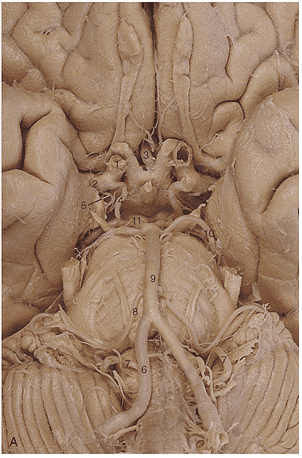
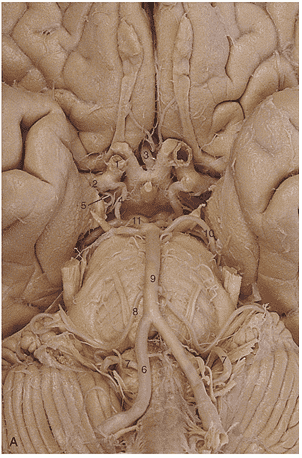
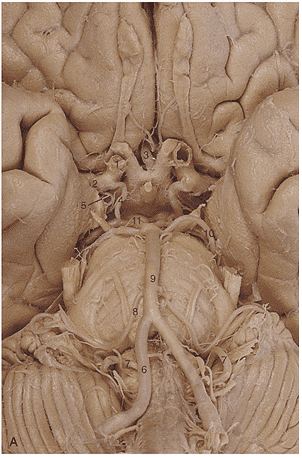
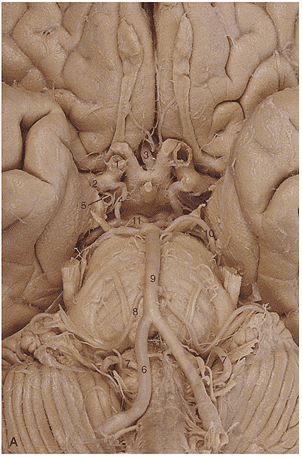
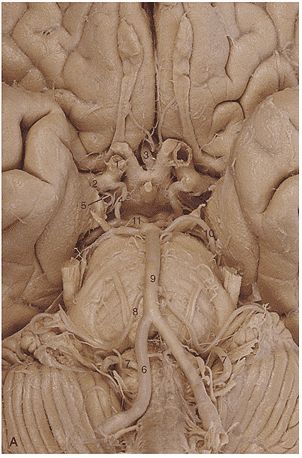
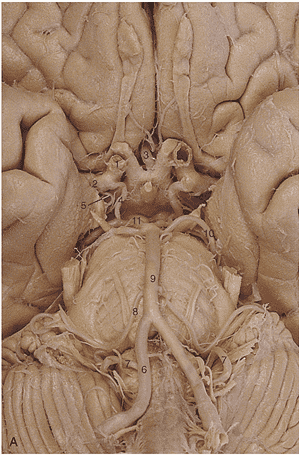
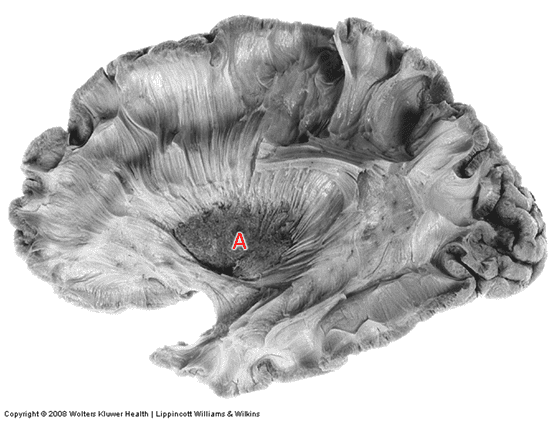
1. In generating this image the _____________ artery was filled with contrast.
Choices:
Answers:
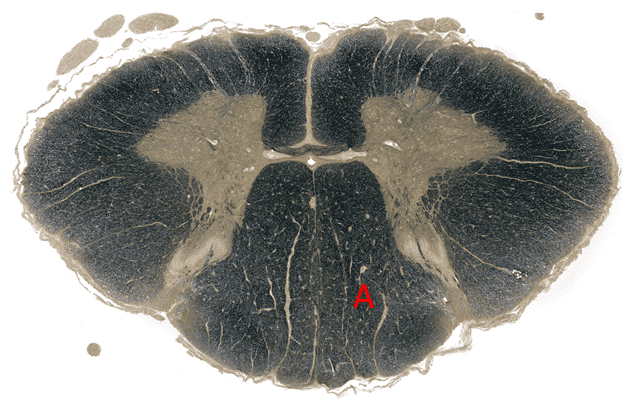
Question 2
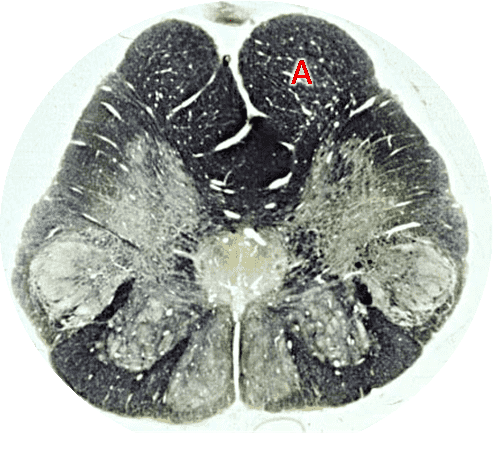
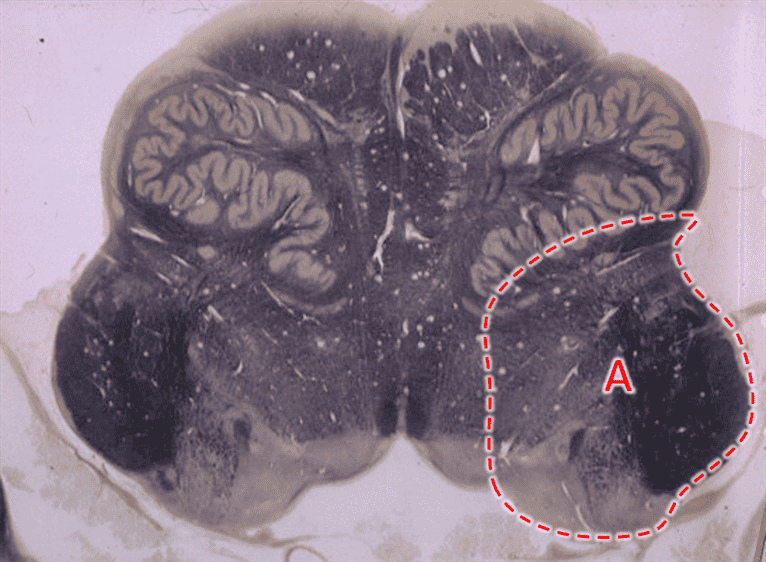
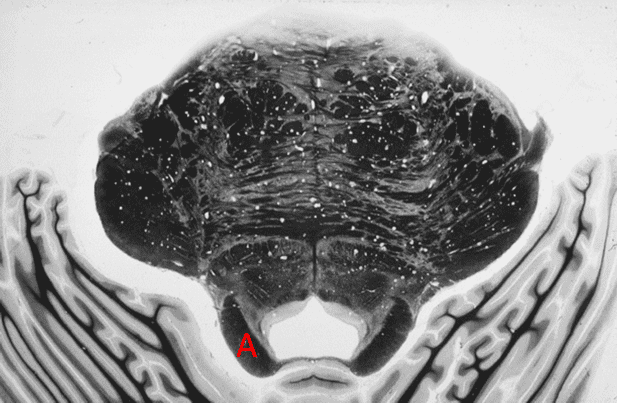
2. Region A is supplied by the _____________ _____________ artery.
Choices:
Answers:
Question 3
3. The arrow is pointing to the ________________ artery.
Choices:
Answers:
Question 4
4. Region A is supplied by the __________ ____________ ____________artery.
Choices:
- posterior inferior cerebellar
Answers:
- posterior inferior cerebellar
Question 5
5. Region A is supplied by the __________ ____________artery.
Choices:
Answers:
Question 6
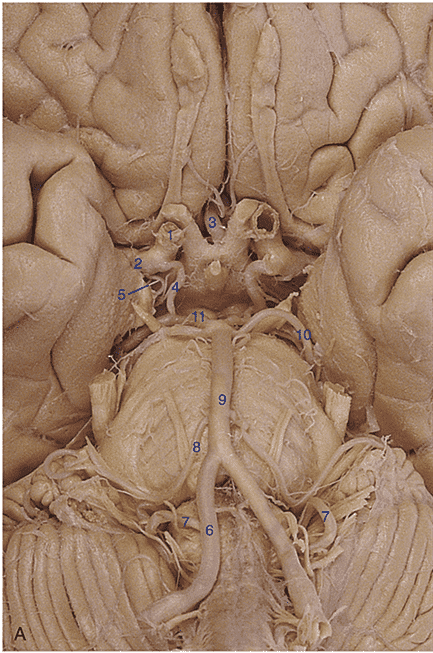
6. Identify artery 1.
Choices:
- internal carotid artery
- middle cerebral artery
- anterior cerebral artery
- posterior communicating artery
- anterior choroidal artery
- vertebral artery
- posterior inferior cerebellar artery
- anterior inferior cerebellar artery
- basilar artery
Answers:
Question 7
7. Identify artery 2.
Choices:
- internal carotid artery
- middle cerebral artery
- anterior cerebral artery
- posterior communicating artery
- anterior choroidal artery
- vertebral artery
- posterior inferior cerebellar artery
- anterior inferior cerebellar artery
- basilar artery
Answers:
Question 8
8. Identify artery 3.
Choices:
- internal carotid artery
- middle cerebral artery
- anterior cerebral artery
- posterior communicating artery
- anterior choroidal artery
- vertebral artery
- posterior inferior cerebellar artery
- anterior inferior cerebellar artery
- basilar artery
Answers:
Question 9
9. Identify artery 4.
Choices:
- internal carotid artery
- middle cerebral artery
- anterior cerebral artery
- posterior communicating artery
- anterior choroidal artery
- vertebral artery
- posterior inferior cerebellar artery
- anterior inferior cerebellar artery
- basilar artery
Answers:
- posterior communicating artery
Question 10
10. Identify artery 5.
Choices:
- internal carotid artery
- middle cerebral artery
- anterior cerebral artery
- posterior communicating artery
- anterior choroidal artery
- vertebral artery
- posterior inferior cerebellar artery
- anterior inferior cerebellar artery
- basilar artery
Answers:
- anterior choroidal artery
Question 11
11. Identify artery 6.
Choices:
- superior cerebellar artery
- posterior cerebral artery
- anterior cerebral artery
- posterior communicating artery
- anterior choroidal artery
- vertebral artery
- posterior inferior cerebellar artery
- anterior inferior cerebellar artery
- basilar artery
Answers:
Question 12
12. Identify artery 7.
Choices:
- superior cerebellar artery
- posterior cerebral artery
- anterior cerebral artery
- posterior communicating artery
- anterior choroidal artery
- vertebral artery
- posterior inferior cerebellar artery
- anterior inferior cerebellar artery
- basilar artery
Answers:
- posterior inferior cerebellar artery
Question 13
13. Identify artery 8.
Choices:
- superior cerebellar artery
- posterior cerebral artery
- anterior cerebral artery
- posterior communicating artery
- anterior choroidal artery
- vertebral artery
- posterior inferior cerebellar artery
- anterior inferior cerebellar artery
- basilar artery
Answers:
- anterior inferior cerebellar artery
Question 14
14. Identify artery 9.
Choices:
- superior cerebellar artery
- posterior cerebral artery
- anterior cerebral artery
- posterior communicating artery
- anterior choroidal artery
- vertebral artery
- posterior inferior cerebellar artery
- anterior inferior cerebellar artery
- basilar artery
Answers:
Question 15
15. Identify artery 10.
Choices:
- superior cerebellar artery
- posterior cerebral artery
- anterior cerebral artery
- anterior communicating artery
- anterior choroidal artery
- vertebral artery
- posterior inferior cerebellar artery
- anterior inferior cerebellar artery
- basilar artery
Answers:
- superior cerebellar artery
Question 16
16. Identify artery 11.
Choices:
- superior cerebellar artery
- posterior cerebral artery
- anterior cerebral artery
- anterior communicating artery
- anterior choroidal artery
- vertebral artery
- posterior inferior cerebellar artery
- anterior inferior cerebellar artery
- basilar artery
Answers:
- posterior cerebral artery
Question 17
17. Region A is supplied by the __________ ____________artery.
Choices:
Answers:
Question 18
18. Region A is supplied by the __________ ____________artery.
Choices:
Answers:
Question 19
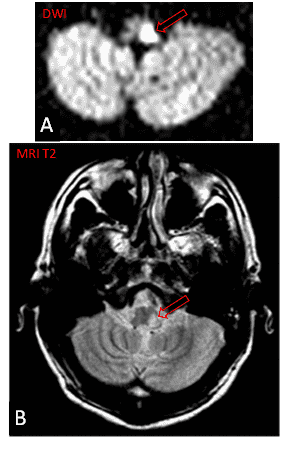
19. The red arrows in these images indicate an infarct of the _________ __________ __________ artery.
Choices:
- posterior inferior cerebellar
Answers:
- posterior inferior cerebellar
Question 20
20. Region A is supplied by the __________ ____________artery.
Choices:
Answers:
Question 1
1. Bundles of subcortical white matter that connect the right and left cerebral hemispheres are called _____________ fibres.
Choices:
Answers:
Question 2
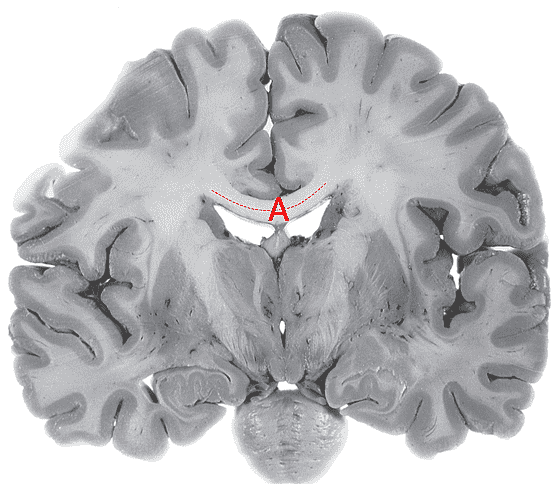
2. The narrowest, and most commonly occluded part of the ventricular system is the ________________ ___________________.
Choices:
Answers:
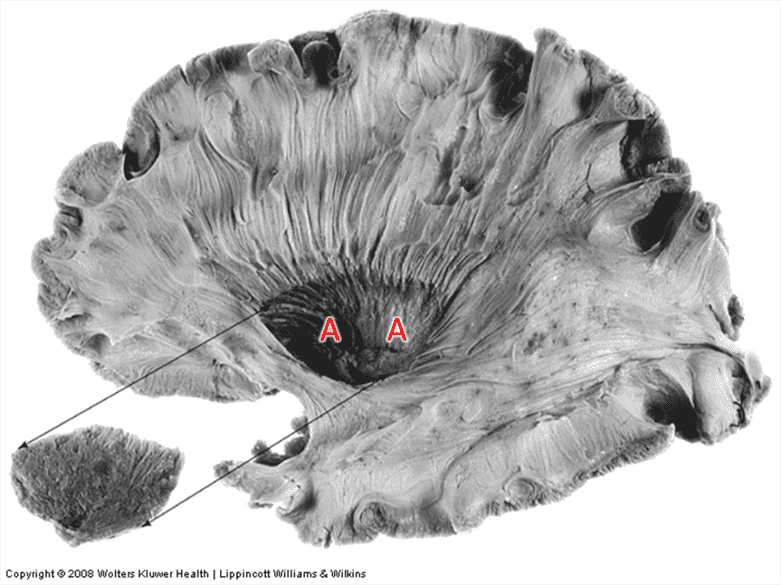
Question 3
3. Identify fibre bundle A.
Choices:
Answers:
Question 4
4. The region where the pons, medulla and cerebellum meet is called the ________________ ______________.
Choices:
Answers:
Question 5
5. The part of the lateral ventricle that extends into the frontal lobe is the ________________ horn.
Choices:
Answers:
Question 6
6. Bundles of subcortical white matter that connect regions of the same cerebral hemisphere are called _____________ fibres.
Choices:
Answers:
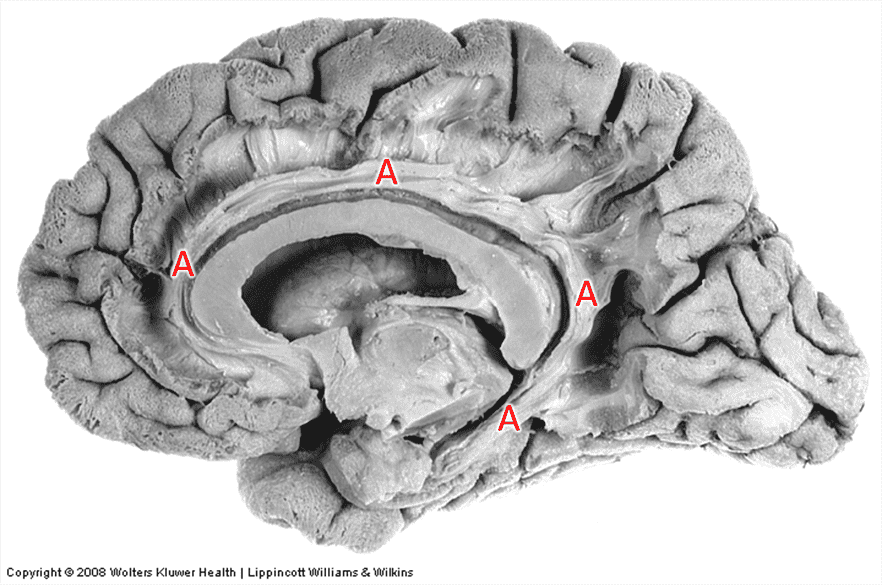
Question 7
7. Identify cortical region A.
Choices:
Answers:
Question 8
8. Bundles of subcortical white matter that connect a cerebral hemisphere with lower centres, such as the brainstem or spinal cord are called _____________ fibres.
Choices:
Answers:
Question 9
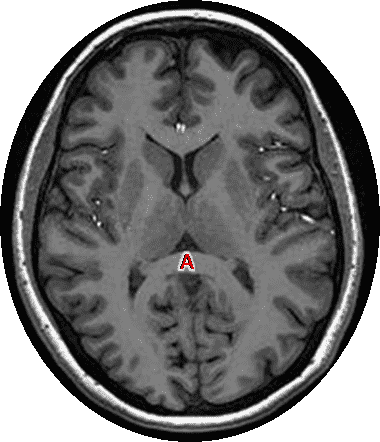
9. Identify white matter structure A.
Choices:
Answers:
Question 10
10. The part of the lateral ventricle that extends into the temporal lobe is the ________________ horn.
Choices:
Answers:
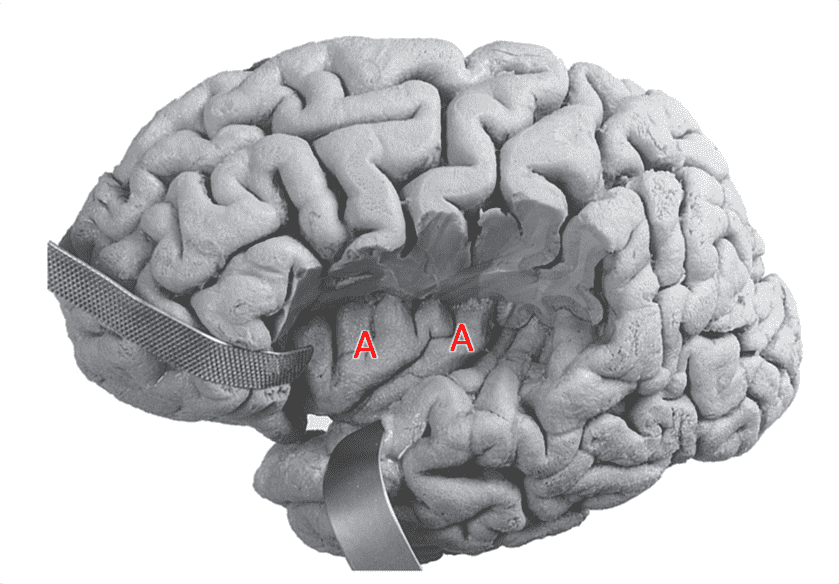
Question 11
11. Identify grey matter structure A. Be specific.
Choices:
Answers:
Question 12
12. Which fibre type forms the cingulum?
Choices:
- association fibres
- commissural fibres
- projection fibres
Answers:
Question 13
13. Brain imaging reveals enlargement of the right and left lateral ventricles, as well as the third ventricle. The fourth ventricle is within normal limits. Where is the obstruction of the vestibular system located?
Choices:
- cerebral aqueduct
- right lateral aperture
- median aperture
- interventricular foramena, bilaterally
Answers:
Question 14
14. The part of the ventricular system associated with the pons and rostral medulla is the ________________ ___________________.
Choices:
Answers:
Question 15
15. Which fibre type forms the corpus callosum?
Choices:
- association fibres
- commissural fibres
- projection fibres
Answers:
Question 16
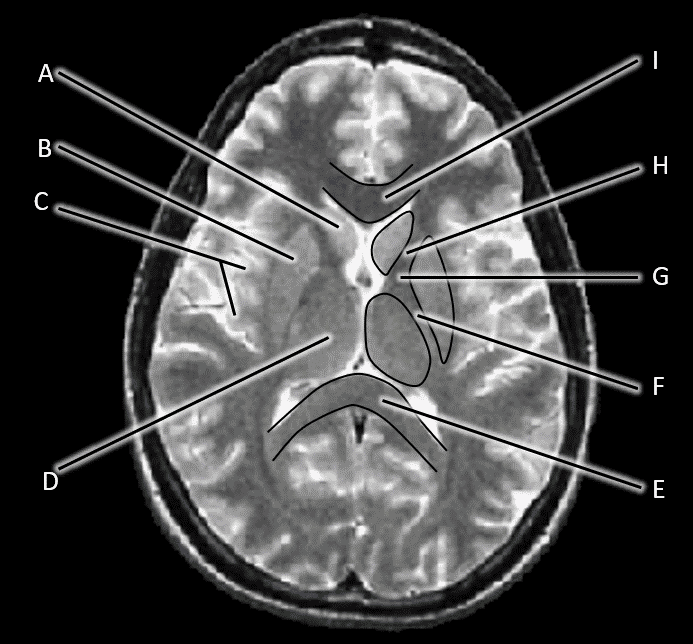
16. Identify A.
Choices:
- head of caudate nucleus
- putamen
- insula
- thalamus
- forceps major
- posterior limb, internal capsule
- genu, internal capsule
- anterior limb, internal capsule
- forceps minor
Answers:
Question 17
17. Identify B.
Choices:
- head of caudate nucleus
- putamen
- insula
- thalamus
- forceps major
- posterior limb, internal capsule
- genu, internal capsule
- anterior limb, internal capsule
- forceps minor
Answers:
Question 18
18. Identify C.
Choices:
- head of caudate nucleus
- putamen
- insula
- thalamus
- forceps major
- posterior limb, internal capsule
- genu, internal capsule
- anterior limb, internal capsule
- forceps minor
Answers:
Question 19
19. Identify D.
Choices:
- head of caudate nucleus
- putamen
- insula
- thalamus
- forceps major
- posterior limb, internal capsule
- genu, internal capsule
- anterior limb, internal capsule
- forceps minor
Answers:
Question 20
20. Identify E.
Choices:
- head of caudate nucleus
- putamen
- insula
- thalamus
- forceps major
- posterior limb, internal capsule
- genu, internal capsule
- anterior limb, internal capsule
- forceps minor
Answers:
Question 21
21. Identify F.
Choices:
- head of caudate nucleus
- putamen
- insula
- thalamus
- forceps major
- posterior limb, internal capsule
- genu, internal capsule
- anterior limb, internal capsule
- forceps minor
Answers:
- posterior limb, internal capsule
Question 22
22. Identify G.
Choices:
- head of caudate nucleus
- putamen
- insula
- thalamus
- forceps major
- posterior limb, internal capsule
- genu, internal capsule
- anterior limb, internal capsule
- forceps minor
Answers:
Question 23
23. Identify H.
Choices:
- head of caudate nucleus
- putamen
- insula
- thalamus
- forceps major
- posterior limb, internal capsule
- genu, internal capsule
- anterior limb, internal capsule
- forceps minor
Answers:
- anterior limb, internal capsule
Question 24
24. Identify I.
Choices:
- thalamus
- forceps major
- head of caudate nucleus
- putamen
- insula
- posterior limb, internal capsule
- genu, internal capsule
- anterior limb, internal capsule
- forceps minor
Answers: